Crystal Structure of Hexokinase KlHxk1 of Kluyveromyces lactis: A MOLECULAR BASIS FOR UNDERSTANDING THE CONTROL OF YEAST HEXOKINASE FUNCTIONS VIA COVALENT MODIFICATION AND OLIGOMERIZATION.
Kuettner, E.B., Kettner, K., Keim, A., Svergun, D.I., Volke, D., Singer, D., Hoffmann, R., Muller, E.C., Otto, A., Kriegel, T.M., Strater, N.(2010) J Biological Chem 285: 41019-41033
- PubMed: 20943665
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.185850
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3O08, 3O1B, 3O1W, 3O4W, 3O5B, 3O6W, 3O80, 3O8M - PubMed Abstract:
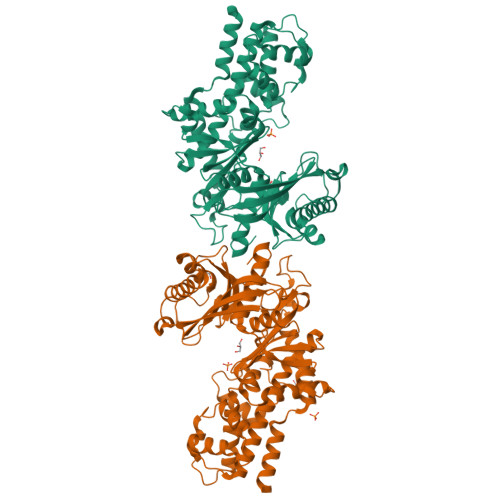
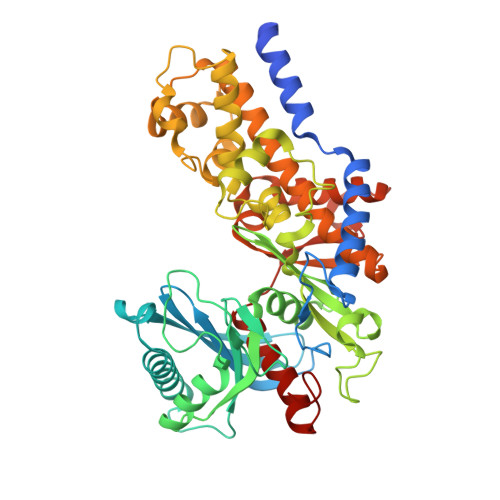
Crystal structures of the unique hexokinase KlHxk1 of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis were determined using eight independent crystal forms. In five crystal forms, a symmetrical ring-shaped homodimer was observed, corresponding to the physiological dimer existing in solution as shown by small-angle x-ray scattering. The dimer has a head-to-tail arrangement such that the small domain of one subunit interacts with the large domain of the other subunit. Dimer formation requires favorable interactions of the 15 N-terminal amino acids that are part of the large domain with amino acids of the small domain of the opposite subunit, respectively. The head-to-tail arrangement involving both domains of the two KlHxk1 subunits is appropriate to explain the reduced activity of the homodimer as compared with the monomeric enzyme and the influence of substrates and products on dimer formation and dissociation. In particular, the structure of the symmetrical KlHxk1 dimer serves to explain why phosphorylation of conserved residue Ser-15 may cause electrostatic repulsions with nearby negatively charged residues of the adjacent subunit, thereby inducing a dissociation of the homologous dimeric hexokinases KlHxk1 and ScHxk2. Two complex structures of KlHxk1 with bound glucose provide a molecular model of substrate binding to the open conformation and the subsequent classical domain closure motion of yeast hexokinases. The entirety of the novel data extends the current concept of glucose signaling in yeast and complements the induced-fit model by integrating the events of N-terminal phosphorylation and dissociation of homodimeric yeast hexokinases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Bioanalytical Chemistry, Center for Biotechnology and Biomedicine, Faculty of Chemistry and Mineralogy, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany.