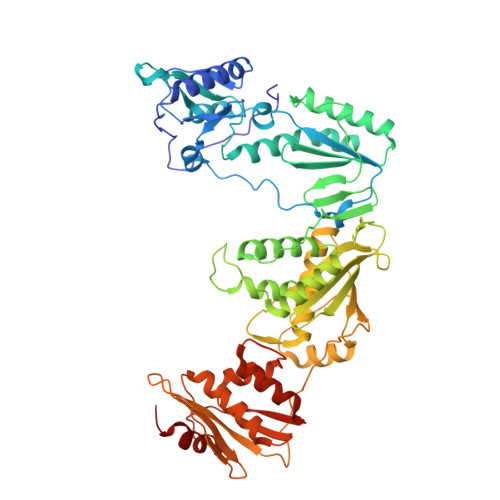
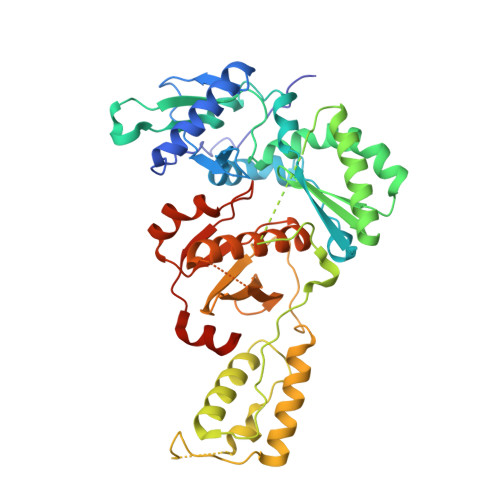
Discovery of piperidin-4-yl-aminopyrimidines as HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. N-benzyl derivatives with broad potency against resistant mutant viruses.
Kertesz, D.J., Brotherton-Pleiss, C., Yang, M., Wang, Z., Lin, X., Qiu, Z., Hirschfeld, D.R., Gleason, S., Mirzadegan, T., Dunten, P.W., Harris, S.F., Villasenor, A.G., Hang, J.Q., Heilek, G.M., Klumpp, K.(2010) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20: 4215-4218
- PubMed: 20538456
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.05.040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3M8P, 3M8Q, 3NBP - PubMed Abstract:
An analysis of the binding motifs of known HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors has led to discovery of novel piperidine-linked aminopyrimidine derivatives with broad activity against wild-type as well as drug-resistant mutant viruses. Notably, the series retains potency against the K103N/Y181C and Y188L mutants, among others. Thus, the N-benzyl compound 5k has a particularly attractive profile. Synthesis and SAR are presented and discussed, as well as crystal structures relating to the binding motifs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Roche Palo Alto LLC, 3431 Hillview Avenue, Palo Alto, CA 94304, USA. deniskertesz@comcast.net