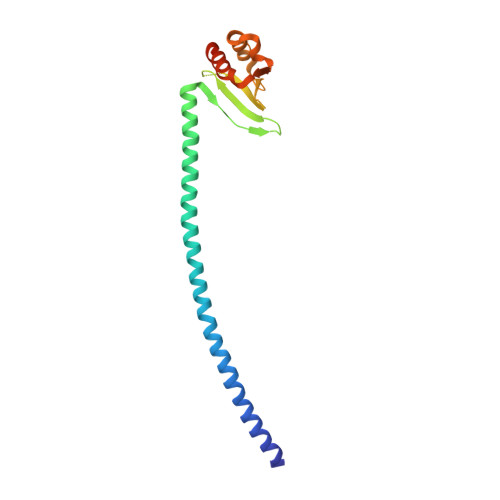
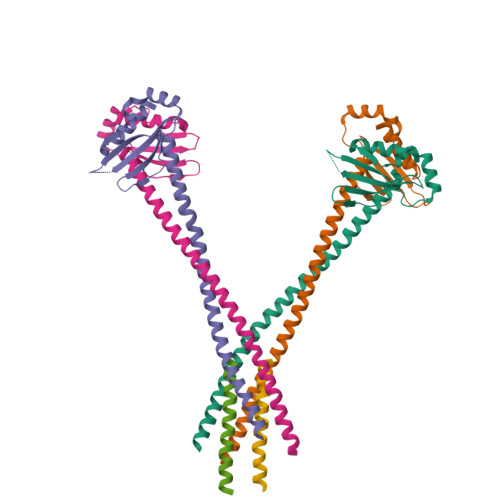The Monopolin Complex Crosslinks Kinetochore Components to Regulate Chromosome-Microtubule Attachments.
Corbett, K.D., Yip, C.K., Ee, L.S., Walz, T., Amon, A., Harrison, S.C.(2010) Cell 142: 556-567
- PubMed: 20723757
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3N4R, 3N4S, 3N4X, 3N7N - PubMed Abstract:
The monopolin complex regulates different types of kinetochore-microtubule attachments in fungi, ensuring sister chromatid co-orientation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae meiosis I and inhibiting merotelic attachment in Schizosaccharomyces pombe mitosis. In addition, the monopolin complex maintains the integrity and silencing of ribosomal DNA (rDNA) repeats in the nucleolus. We show here that the S. cerevisiae Csm1/Lrs4 monopolin subcomplex has a distinctive V-shaped structure, with two pairs of protein-protein interaction domains positioned approximately 10 nm apart. Csm1 presents a conserved hydrophobic surface patch that binds two kinetochore proteins: Dsn1, a subunit of the outer-kinetochore MIND/Mis12 complex, and Mif2/CENP-C. Csm1 point-mutations that disrupt kinetochore-subunit binding also disrupt sister chromatid co-orientation in S. cerevisiae meiosis I. We further show that the same Csm1 point-mutations affect rDNA silencing, probably by disrupting binding to the rDNA-associated protein Tof2. We propose that Csm1/Lrs4 functions as a molecular clamp, crosslinking kinetochore components to enforce sister chromatid co-orientation in S. cerevisiae meiosis I and to suppress merotelic attachment in S. pombe mitosis, and crosslinking rDNA repeats to aid rDNA silencing.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Harvard Medical School, 250 Longwood Avenue, Boston, MA 02115, USA.