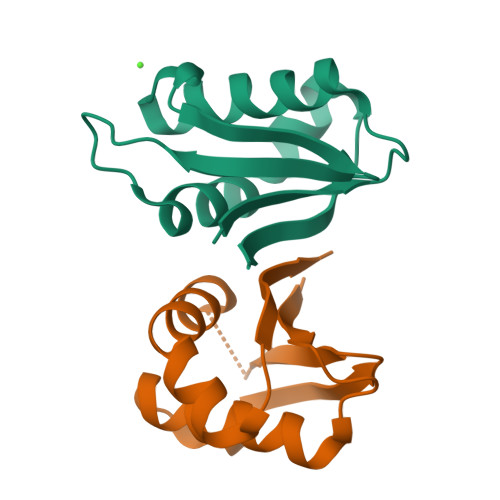
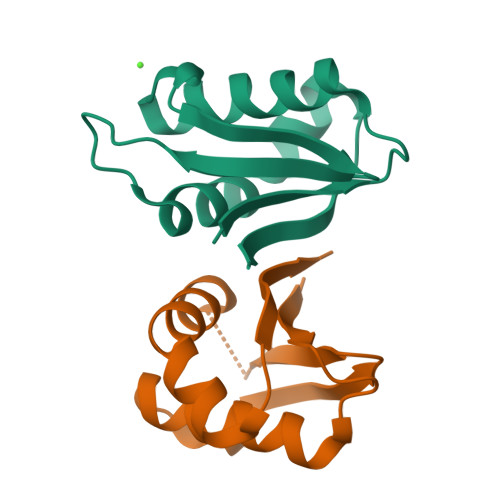
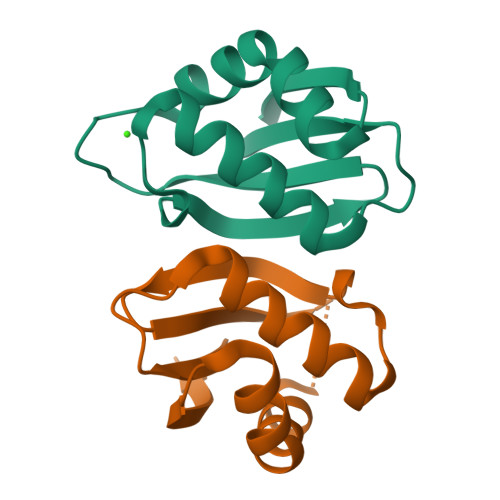
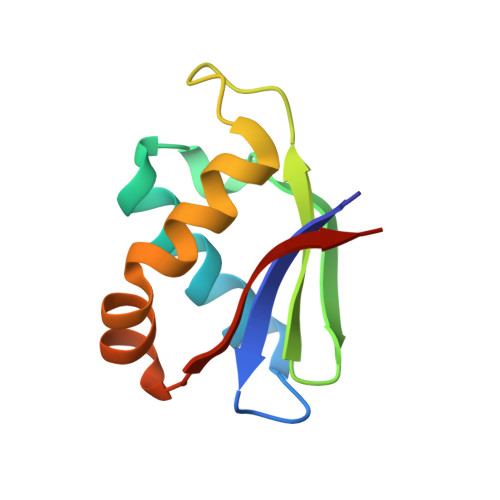
Structure of the mature ectodomain of the human receptor-type protein-tyrosine phosphatase IA-2.
Primo, M.E., Klinke, S., Sica, M.P., Goldbaum, F.A., Jakoncic, J., Poskus, E., Ermacora, M.R.(2008) J Biological Chem 283: 4674-4681
- PubMed: 18048354
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M708144200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QT7, 3N4W, 3NG8 - PubMed Abstract:
IA-2 (insulinoma-associated protein 2) is a protein-tyrosine phosphatase receptor located in secretory granules of neuroendocrine cells. Initially, it attracted attention due to its involvement in the autoimmune response associated to diabetes. Later it was found that upon exocytosis, the cytoplasmic domain of IA-2 is cleaved and relocated to the nucleus, where it enhances the transcription of the insulin gene. A concerted functioning of the whole receptor is to be expected. However, very little is known about the structure and function of the transmembrane and extracellular domains of IA-2. To address this issue, we solved the x-ray structure of the mature ectodomain of IA-2 (meIA-2) to 1.30A resolution. The fold of meIA-2 is related to the SEA (sea urchin sperm protein, enterokinase, agrin)) domains of mucins, suggesting its participation in adhesive contacts to the extracellular matrix and providing clues on how this kind of molecule may associate and form homo- and heterodimers. Moreover, we discovered that meIA-2 is self-proteolyzed in vitro by reactive oxygen species, suggesting the possibility of a new shedding mechanism that might be significant in normal function or pathological processes. Knowledge of meIA-2 structure should facilitate the search of its possible ligands and molecular interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (Conicet), Rivadavia 1917 C1033AAJ, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires, Argentina.