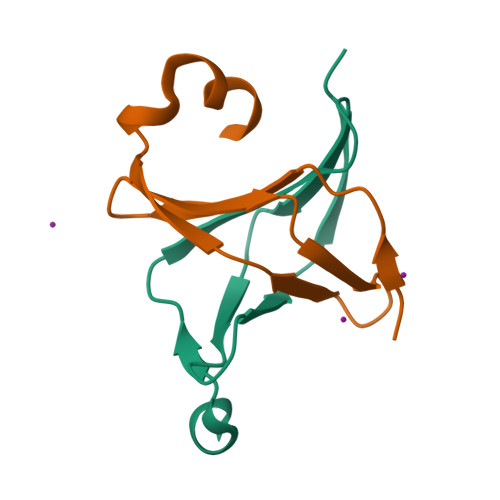
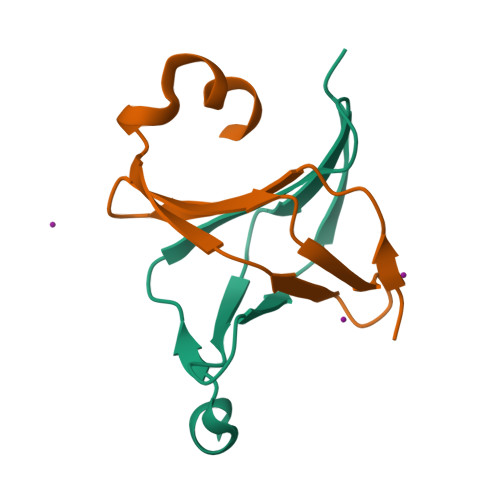
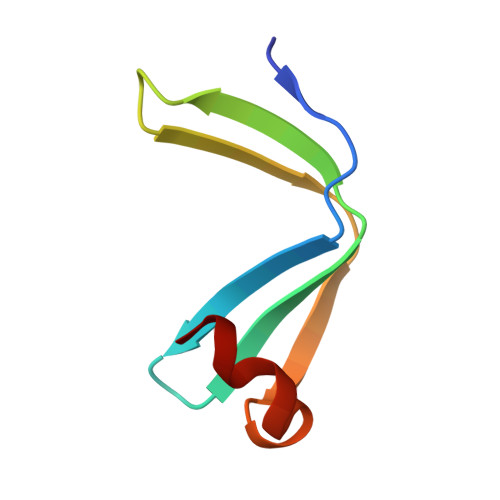
Crystal structures of NAC domains of human nascent polypeptide-associated complex (NAC) and its alphaNAC subunit
Wang, L.F., Zhang, W.C., Wang, L., Zhang, X.J.C., Li, X.M., Rao, Z.(2010) Protein Cell 1: 406-416
- PubMed: 21203952
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-010-0049-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3MCB, 3MCE - PubMed Abstract:
Nascent polypeptide associated complex (NAC) and its two isolated subunits, αNAC and βNAC, play important roles in nascent peptide targeting. We determined a 1.9 Å resolution crystal structure of the interaction core of NAC heterodimer and a 2.4 Å resolution crystal structure of αNAC NAC domain homodimer. These structures provide detailed information of NAC heterodimerization and αNAC homodimerization. We found that the NAC domains of αNAC and βNAC share very similar folding despite of their relative low identity of amino acid sequences. Furthermore, different electric charge distributions of the two subunits at the NAC interface provide an explanation to the observation that the heterodimer of NAC complex is more stable than the single subunit homodimer. In addition, we successfully built a βNAC NAC domain homodimer model based on homologous modeling, suggesting that NAC domain dimerization is a general property of the NAC family. These 3D structures allow further studies on structure-function relationship of NAC.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 15 Datun Road, Beijing, 100101, China.