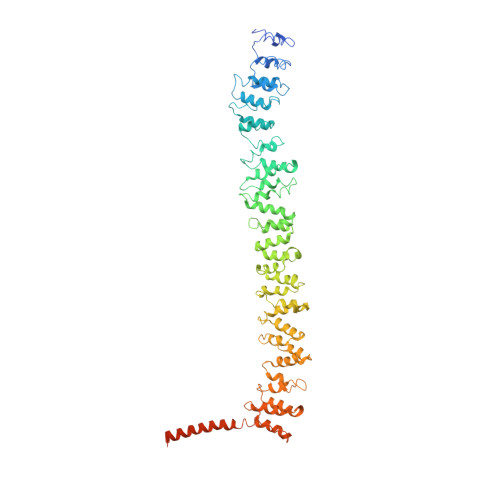
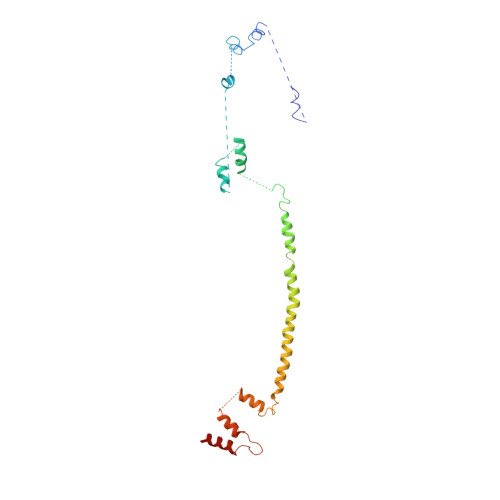
Conformation switching of clathrin light chain regulates clathrin lattice assembly.
Wilbur, J.D., Hwang, P.K., Ybe, J.A., Lane, M., Sellers, B.D., Jacobson, M.P., Fletterick, R.J., Brodsky, F.M.(2010) Dev Cell 18: 841-848
- PubMed: 20493816
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2010.04.007
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LVG, 3LVH - PubMed Abstract:
Clathrin-coated vesicle formation is responsible for membrane traffic to and from the endocytic pathway during receptor-mediated endocytosis and organelle biogenesis, influencing how cells relate to their environment. Generating these vesicles involves self-assembly of clathrin molecules into a latticed coat on membranes that recruits receptors and organizes protein machinery necessary for budding. Here we define a molecular mechanism regulating clathrin lattice formation by obtaining structural information from co-crystals of clathrin subunits. Low resolution X-ray diffraction data (7.9-9.0 A) was analyzed using a combination of molecular replacement with an energy-minimized model and noncrystallographic symmetry averaging. Resulting topological information revealed two conformations of the regulatory clathrin light chain bound to clathrin heavy chain. Based on protein domain positions, mutagenesis, and biochemical assays, we identify an electrostatic interaction between the clathrin subunits that allows the observed conformational variation in clathrin light chains to alter the conformation of the clathrin heavy chain and thereby regulates assembly.
- Graduate Program in Biophysics, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA 94143, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: