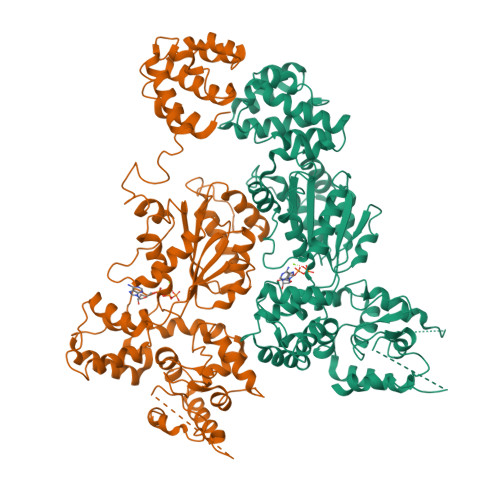
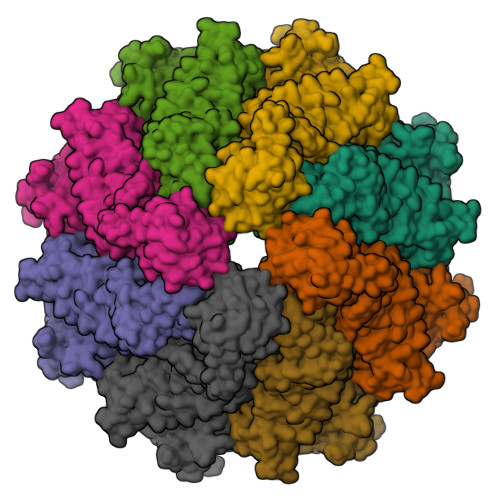
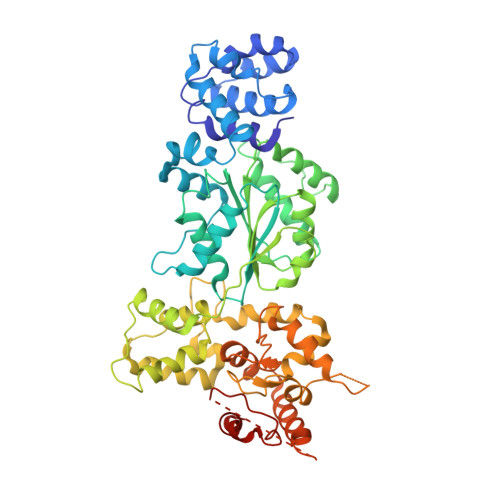
Crystal structure of the Caenorhabditis elegans apoptosome reveals an octameric assembly of CED-4.
Qi, S., Pang, Y., Hu, Q., Liu, Q., Li, H., Zhou, Y., He, T., Liang, Q., Liu, Y., Yuan, X., Luo, G., Li, H., Wang, J., Yan, N., Shi, Y.(2010) Cell 141: 446-457
- PubMed: 20434985
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LQQ, 3LQR - PubMed Abstract:
The CED-4 homo-oligomer or apoptosome is required for initiation of programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans by facilitating autocatalytic activation of the CED-3 caspase zymogen. How the CED-4 apoptosome assembles and activates CED-3 remains enigmatic. Here we report the crystal structure of the complete CED-4 apoptosome and show that it consists of eight CED-4 molecules, organized as a tetramer of an asymmetric dimer via a previously unreported interface among AAA(+) ATPases. These eight CED-4 molecules form a funnel-shaped structure. The mature CED-3 protease is monomeric in solution and forms an active holoenzyme with the CED-4 apoptosome, within which the protease activity of CED-3 is markedly stimulated. Unexpectedly, the octameric CED-4 apoptosome appears to bind only two, not eight, molecules of mature CED-3. The structure of the CED-4 apoptosome reveals shared principles for the NB-ARC family of AAA(+) ATPases and suggests a mechanism for the activation of CED-3.
Organizational Affiliation:
Ministry of Education Protein Science Laboratory, School of Life Sciences and School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China.