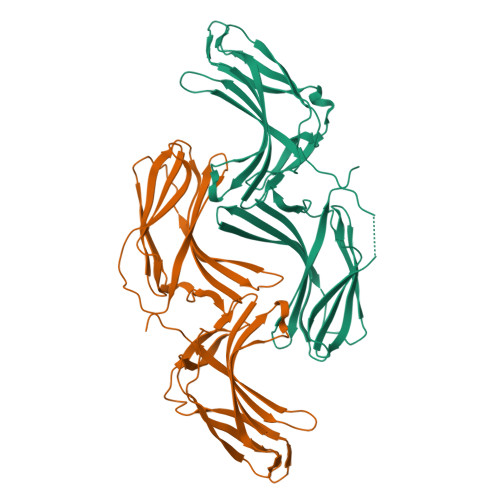
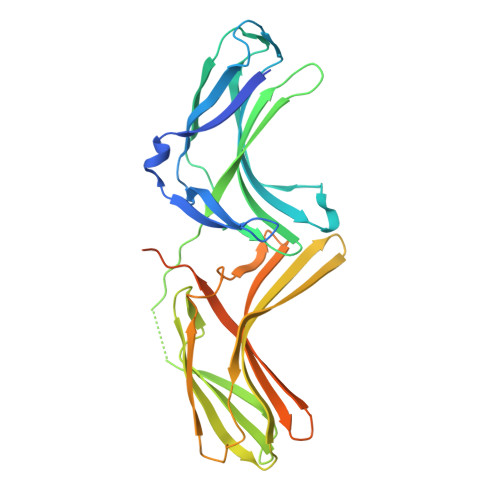
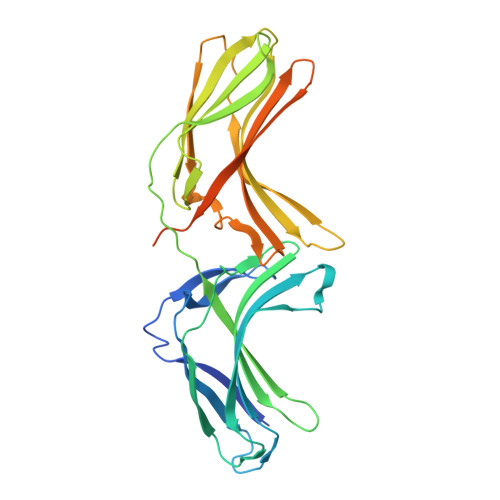
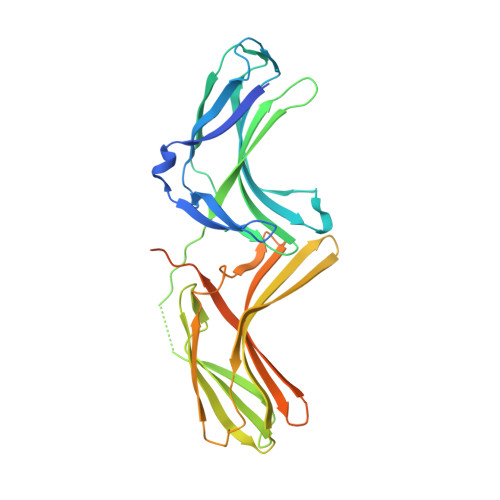
Assembly and solution structure of the core retromer protein complex.
Norwood, S.J., Shaw, D.J., Cowieson, N.P., Owen, D.J., Teasdale, R.D., Collins, B.M.(2011) Traffic 12: 56-71
- PubMed: 20875039
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01124.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LH8, 3LH9, 3LHA - PubMed Abstract:
Retromer is a peripheral membrane protein complex that has pleiotropic roles in endosomal membrane trafficking. The core of retromer possesses three subunits, VPS35, VPS29 and VPS26, that play different roles in binding to cargo, regulatory proteins and complex stabilization. We have performed an investigation of the thermodynamics of core retromer assembly using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) demonstrating that VPS35 acts as the central subunit to which VPS29 and VPS26 bind independently. Furthermore, we confirm that the conserved PRLYL motif of the large VPS35 subunit is critical for direct VPS26 interaction. Heat capacity measurements of VPS29 and VPS26 binding to VPS35 indicate extensive binding interfaces and suggest conformational alterations in VPS29 or VPS35 upon complex formation. Solution studies of the retromer core using small-angle X-ray scattering allow us to propose a model whereby VPS35 forms an extended platform with VPS29 and VPS26 bound at distal ends, with the potential for forming dimeric assemblies.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland 4072, Australia.