A joint x-ray and neutron study on amicyanin reveals the role of protein dynamics in electron transfer.
Sukumar, N., Mathews, F.S., Langan, P., Davidson, V.L.(2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 6817-6822
- PubMed: 20351252
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912672107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3L45 - PubMed Abstract:
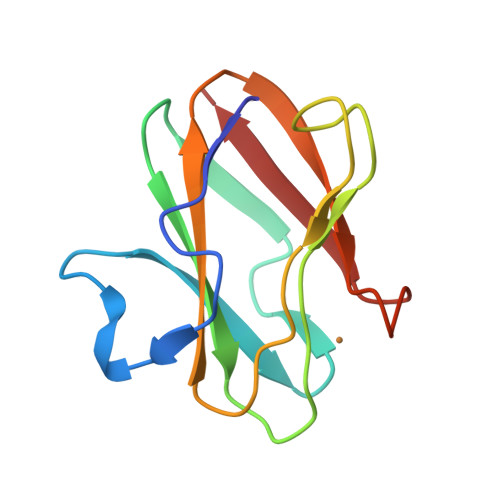
The joint x-ray/neutron diffraction model of the Type I copper protein, amicyanin from Paracoccus denitrificans was determined at 1.8 A resolution. The protein was crystallized using reagents prepared in D(2)O. About 86% of the amide hydrogen atoms are either partially or fully exchanged, which correlates well with the atomic depth of the amide nitrogen atom and the secondary structure type, but with notable exceptions. Each of the four residues that provide copper ligands is partially deuterated. The model reveals the dynamic nature of the protein, especially around the copper-binding site. A detailed analysis of the presence of deuterated water molecules near the exchange sites indicates that amide hydrogen exchange is primarily due to the flexibility of the protein. Analysis of the electron transfer path through the protein shows that residues in that region are highly dynamic, as judged by hydrogen/deuterium exchange. This could increase the rate of electron transfer by transiently shortening through-space jumps in pathways or by increasing the atomic packing density. Analysis of C-HX bonding reveals previously undefined roles of these relatively weak H bonds, which, when present in sufficient number can collectively influence the structure, redox, and electron transfer properties of amicyanin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Northeastern Collaborative Access Team and Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Cornell University, Building 436E, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL 60439, USA. sukumar@anl.gov