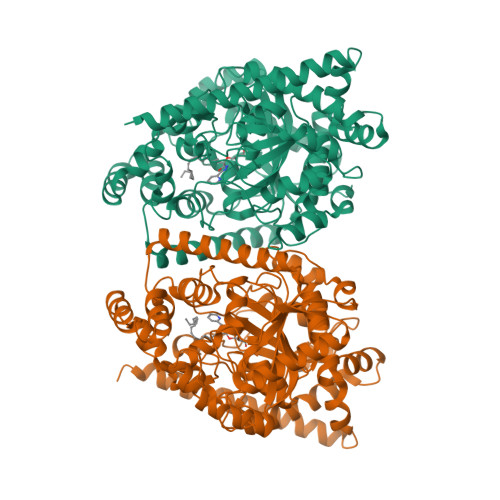
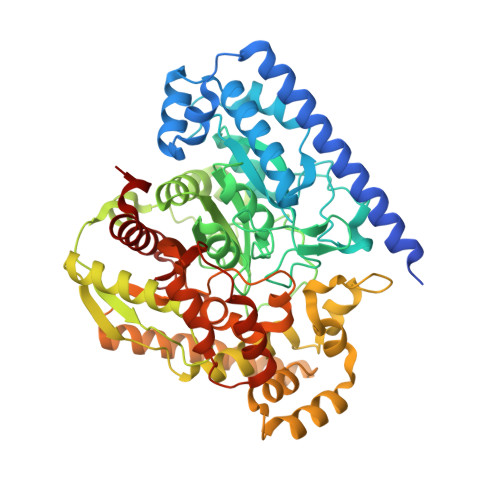
X-ray crystallographic analysis of alpha-ketoheterocycle inhibitors bound to a humanized variant of fatty acid amide hydrolase.
Mileni, M., Garfunkle, J., Ezzili, C., Kimball, F.S., Cravatt, B.F., Stevens, R.C., Boger, D.L.(2010) J Med Chem 53: 230-240
- PubMed: 19924997
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm9012196
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3K7F, 3K83, 3K84 - PubMed Abstract:
Three cocrystal X-ray structures of the alpha-ketoheterocycle inhibitors 3-5 bound to a humanized variant of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) are disclosed and comparatively discussed alongside those of 1 (OL-135) and its isomer 2. These five X-ray structures systematically probe each of the three active site regions key to substrate or inhibitor binding: (1) the conformationally mobile acyl chain-binding pocket and membrane access channel responsible for fatty acid amide substrate and inhibitor acyl chain binding, (2) the atypical active site catalytic residues and surrounding oxyanion hole that covalently binds the core of the alpha-ketoheterocycle inhibitors captured as deprotonated hemiketals mimicking the tetrahedral intermediate of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction, and (3) the cytosolic port and its uniquely important imbedded ordered water molecules and a newly identified anion binding site. The detailed analysis of their key active site interactions and their implications on the interpretation of the available structure-activity relationships are discussed providing important insights for future design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, The Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology,The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, California 92037, USA.