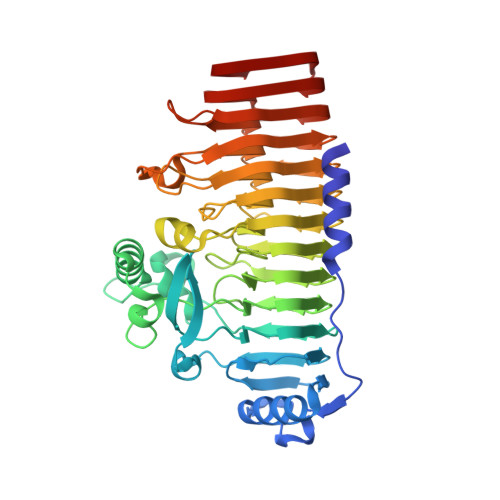
The crystal structure of a hyperthermoactive exopolygalacturonase from Thermotoga maritima reveals a unique tetramer
Pijning, T., van Pouderoyen, G., Kluskens, L., van der Oost, J., Dijkstra, B.W.(2009) FEBS Lett
- PubMed: 19854184
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.10.047
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3JUR - PubMed Abstract:
The exopolygalacturonase from Thermotoga maritima is the most thermoactive and thermostable pectinase known to date. Here we present its crystal structure at 2.05A resolution. High structural homology around the active site allowed us to propose a model for substrate binding, explaining the exo-cleavage activity and specificity for non-methylated saturated galacturonate at the non-reducing end. Furthermore, the structure reveals unique features that contribute to the formation of stable tetramers in solution. Such an oligomerization has not been observed before for polygalacturonases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Biophysical Chemistry, University of Groningen, Nijenborgh 4, 9747 AG Groningen, The Netherlands.