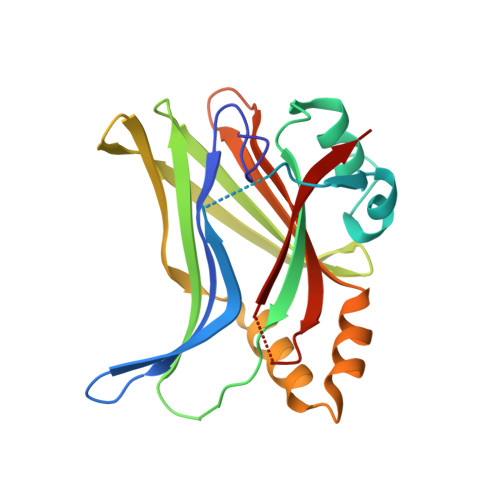
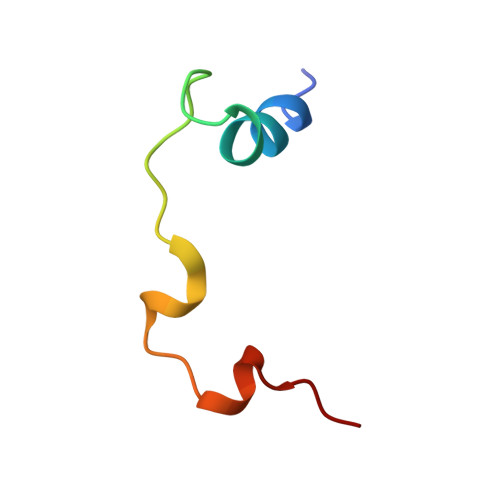
Structural basis of YAP recognition by TEAD4 in the hippo pathway.
Chen, L., Chan, S.W., Zhang, X., Walsh, M., Lim, C.J., Hong, W., Song, H.(2010) Genes Dev 24: 290-300
- PubMed: 20123908
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1865310
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3JUA - PubMed Abstract:
The Hippo signaling pathway controls cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis by regulating the expression of target genes that execute these processes. Acting downstream from this pathway is the YAP transcriptional coactivator, whose biological function is mediated by the conserved TEAD family transcription factors. The interaction of YAP with TEADs is critical to regulate Hippo pathway-responsive genes. Here, we describe the crystal structure of the YAP-interacting C-terminal domain of TEAD4 in complex with the TEAD-interacting N-terminal domain of YAP. The structure reveals that the N-terminal region of YAP is folded into two short helices with an extended loop containing the PXXPhiP motif in between, while the C-terminal domain of TEAD4 has an immunoglobulin-like fold. YAP interacts with TEAD4 mainly through the two short helices. Point mutations of TEAD4 indicate that the residues important for YAP interaction are required for its transforming activity. Mutagenesis reveals that the PXXPhiP motif of YAP, although making few contacts with TEAD4, is important for TEAD4 interaction as well as for the transforming activity.
- The Cancer and Developmental Cell Biology Division, Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, Proteos, Singapore.
Organizational Affiliation: