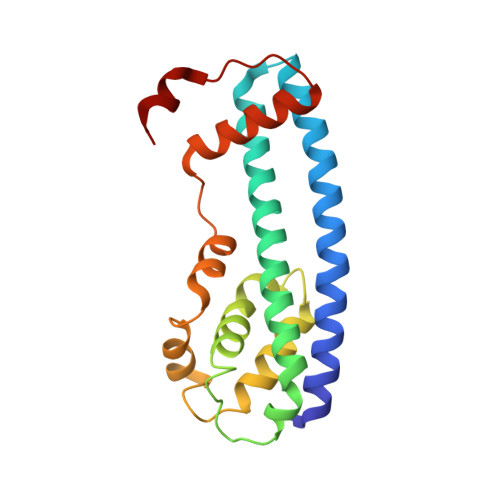
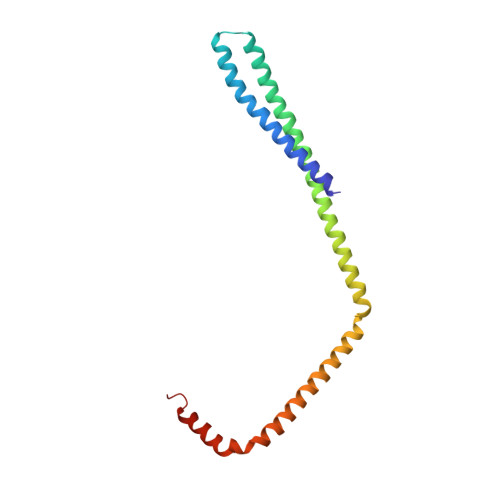
Structure and membrane remodeling activity of ESCRT-III helical polymers.
McCullough, J., Clippinger, A.K., Talledge, N., Skowyra, M.L., Saunders, M.G., Naismith, T.V., Colf, L.A., Afonine, P., Arthur, C., Sundquist, W.I., Hanson, P.I., Frost, A.(2015) Science 350: 1548-1551
- PubMed: 26634441
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad8305
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3JC1 - PubMed Abstract:
The endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRT) proteins mediate fundamental membrane remodeling events that require stabilizing negative membrane curvature. These include endosomal intralumenal vesicle formation, HIV budding, nuclear envelope closure, and cytokinetic abscission. ESCRT-III subunits perform key roles in these processes by changing conformation and polymerizing into membrane-remodeling filaments. Here, we report the 4 angstrom resolution cryogenic electron microscopy reconstruction of a one-start, double-stranded helical copolymer composed of two different human ESCRT-III subunits, charged multivesicular body protein 1B (CHMP1B) and increased sodium tolerance 1 (IST1). The inner strand comprises "open" CHMP1B subunits that interlock in an elaborate domain-swapped architecture and is encircled by an outer strand of "closed" IST1 subunits. Unlike other ESCRT-III proteins, CHMP1B and IST1 polymers form external coats on positively curved membranes in vitro and in vivo. Our analysis suggests how common ESCRT-III filament architectures could stabilize different degrees and directions of membrane curvature.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT 84112, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: