P22 coat protein structures reveal a novel mechanism for capsid maturation: stability without auxiliary proteins or chemical crosslinks
Parent, K.N., Khayat, R., Tu, L.H., Suhanovsky, M.M., Cortines, J.R., Teschke, C.M., Johnson, J.E., Baker, T.S.(2010) Structure 18: 390-401
- PubMed: 20223221
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2009.12.014
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3IYH, 3IYI - PubMed Abstract:
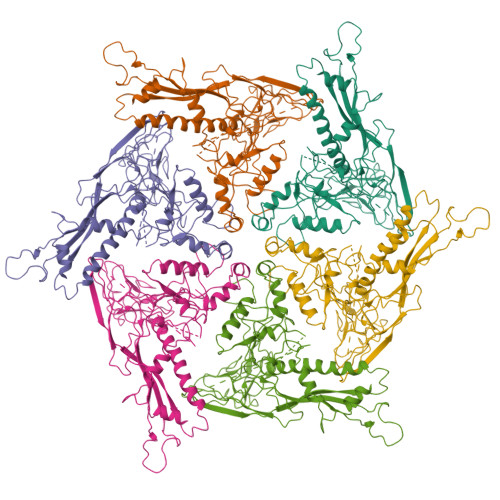
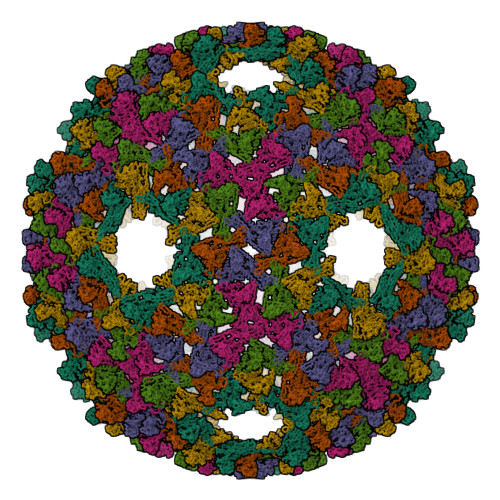
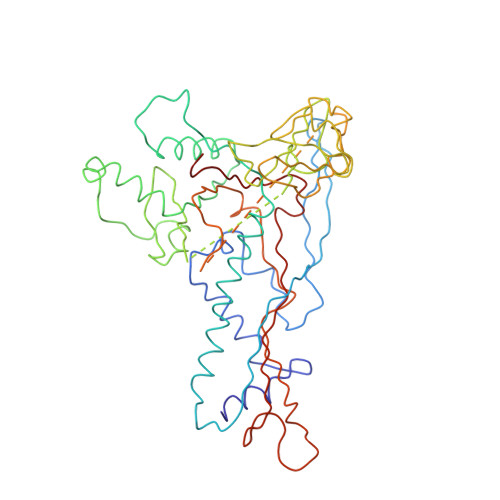
Viral capsid assembly and stability in tailed, dsDNA phage and Herpesviridae are achieved by various means including chemical crosslinks (unique to HK97), or auxiliary proteins (lambda, T4, phi29, and herpesviruses). All these viruses have coat proteins (CP) with a conserved, HK97-like core structure. We used a combination of trypsin digestion, gold labeling, cryo-electron microscopy, 3D image reconstruction, and comparative modeling to derive two independent, pseudoatomic models of bacteriophage P22 CP: before and after maturation. P22 capsid stabilization results from intersubunit interactions among N-terminal helices and an extensive "P loop," which obviate the need for crosslinks or auxiliary proteins. P22 CP also has a telokin-like Ig domain that likely stabilizes the monomer fold so that assembly may proceed via individual subunit addition rather than via preformed capsomers as occurs in HK97. Hence, the P22 CP structure may be a paradigm for understanding how monomers assemble in viruses like phi29 and HSV-1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry & Biochemistry, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA 92093, USA.