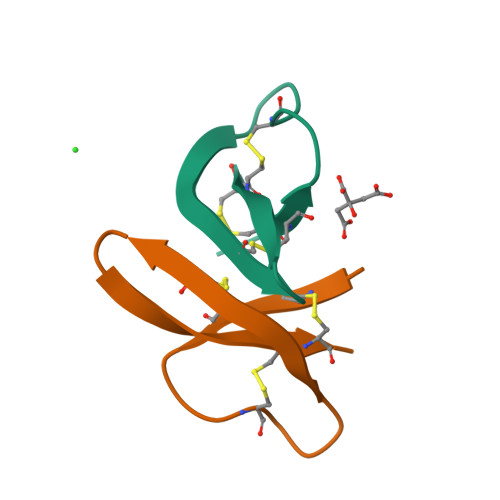
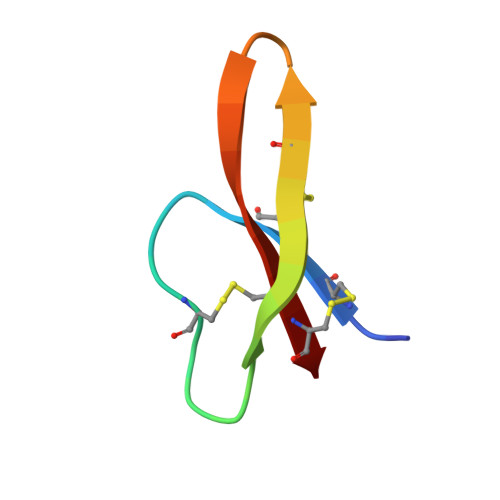
Selective arginines are important for the antibacterial activity and host cell interaction of human alpha-defensin 5
de Leeuw, E., Rajabi, M., Zou, G., Pazgier, M., Lu, W.(2009) FEBS Lett 583: 2507-2512
- PubMed: 19589339
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.06.051
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3I5W - PubMed Abstract:
Defensins constitute a major family of natural antimicrobial peptides that protect the host against microbial invasion. Here, we report on the antibacterial properties and cellular interaction of Human Defensin 5 as a function of its positive charge and hydrophobicity. We find that selective replacement of arginine residues in HD-5 by alanine or charge-neutral lysine residues reduces antibacterial killing as well as host cell interaction. We identify arginines at positions 9 and 28 in the HD-5 sequence as particularly important for its function. Replacement of arginine at position 13 to Histidine, as observed in a Crohn's disease patient, reduced bacterial killing strain-selectively. Finally, we find that HD-5 interacts with host cells via receptor-mediated mechanisms.
Organizational Affiliation:
University of Maryland Baltimore School of Medicine, Institute of Human Virology, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Baltimore, MD 21201, USA. edeleeuw2@ihv.umaryland.edu