The protective antigen component of anthrax toxin forms functional octameric complexes.
Kintzer, A.F., Thoren, K.L., Sterling, H.J., Dong, K.C., Feld, G.K., Tang, I.I., Zhang, T.T., Williams, E.R., Berger, J.M., Krantz, B.A.(2009) J Mol Biol 392: 614-629
- PubMed: 19627991
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.07.037
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
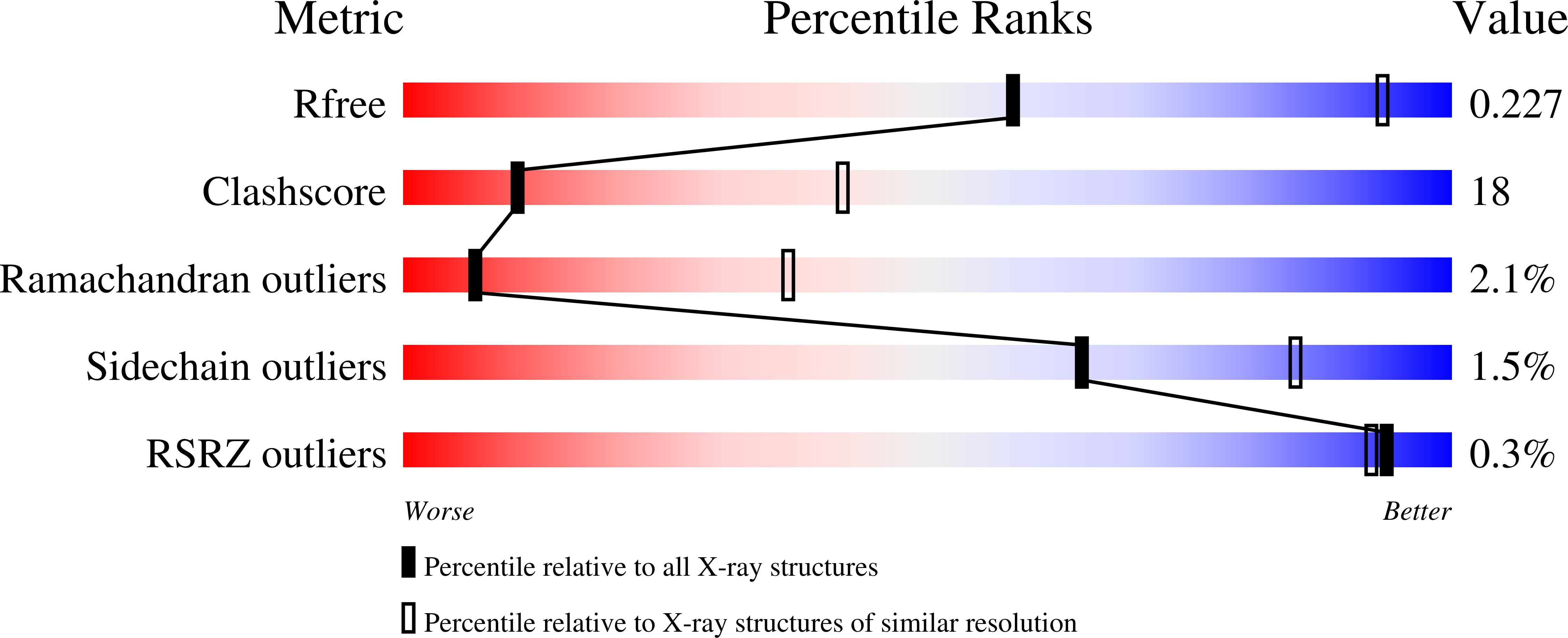
3HVD - PubMed Abstract:
The assembly of bacterial toxins and virulence factors is critical to their function, but the regulation of assembly during infection has not been studied. We begin to address this question using anthrax toxin as a model. The protective antigen (PA) component of the toxin assembles into ring-shaped homooligomers that bind the two other enzyme components of the toxin, lethal factor (LF) and edema factor (EF), to form toxic complexes. To disrupt the host, these toxic complexes are endocytosed, such that the PA oligomer forms a membrane-spanning channel that LF and EF translocate through to enter the cytosol. Using single-channel electrophysiology, we show that PA channels contain two populations of conductance states, which correspond to two different PA pre-channel oligomers observed by electron microscopy-the well-described heptamer and a novel octamer. Mass spectrometry demonstrates that the PA octamer binds four LFs, and assembly routes leading to the octamer are populated with even-numbered, dimeric and tetrameric, PA intermediates. Both heptameric and octameric PA complexes can translocate LF and EF with similar rates and efficiencies. Here, we report a 3.2-A crystal structure of the PA octamer. The octamer comprises approximately 20-30% of the oligomers on cells, but outside of the cell, the octamer is more stable than the heptamer under physiological pH. Thus, the PA octamer is a physiological, stable, and active assembly state capable of forming lethal toxins that may withstand the hostile conditions encountered in the bloodstream. This assembly mechanism may provide a novel means to control cytotoxicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of California, Berkeley, 94720, USA.