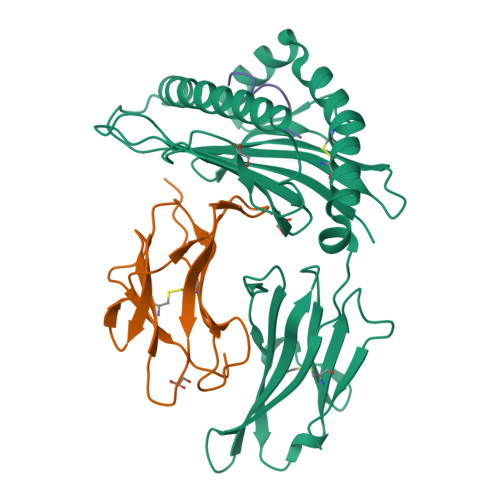
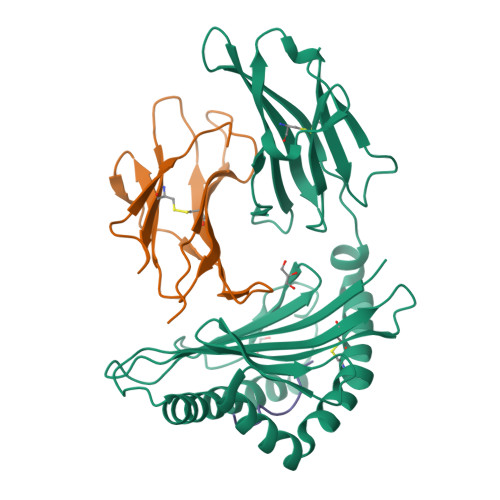
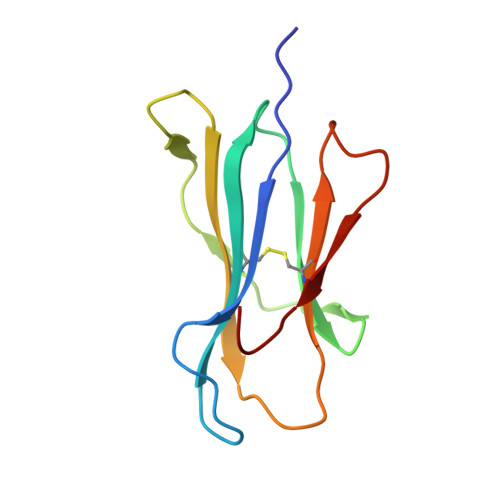
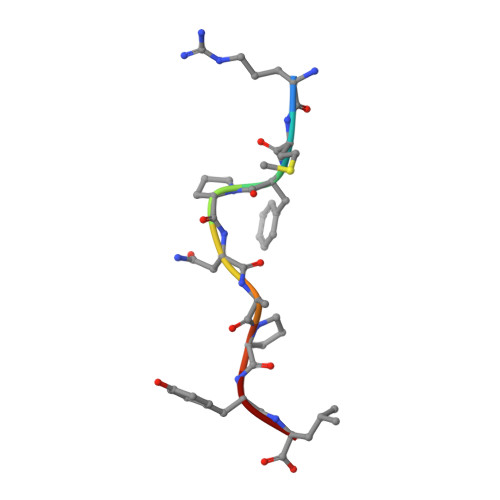
Structures of native and affinity-enhanced WT1 epitopes bound to HLA-A*0201: Implications for WT1-based cancer therapeutics.
Borbulevych, O.Y., Do, P., Baker, B.M.(2010) Mol Immunol 47: 2519-2524
- PubMed: 20619457
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2010.06.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HPJ, 3MYJ - PubMed Abstract:
Presentation of peptides by class I or class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules is required for the initiation and propagation of a T cell-mediated immune response. Peptides from the Wilms Tumor 1 transcription factor (WT1), upregulated in many hematopoetic and solid tumors, can be recognized by T cells and numerous efforts are underway to engineer WT1-based cancer vaccines. Here we determined the structures of the class I MHC molecule HLA-A*0201 bound to the native 126-134 epitope of the WT1 peptide and a recently described variant (R1Y) with improved MHC binding. The R1Y variant, a potential vaccine candidate, alters the positions of MHC charged side chains near the peptide N-terminus and significantly reduces the peptide/MHC electrostatic surface potential. These alterations indicate that the R1Y variant is an imperfect mimic of the native WT1 peptide, and suggest caution in its use as a therapeutic vaccine. Stability measurements revealed how the R1Y substitution enhances MHC binding affinity, and together with the structures suggest a strategy for engineering WT1 variants with improved MHC binding that retain the structural features of the native peptide/MHC complex.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Notre Dame, 251 Nieuwland Science Hall, Notre Dame, IN 46556, United States.