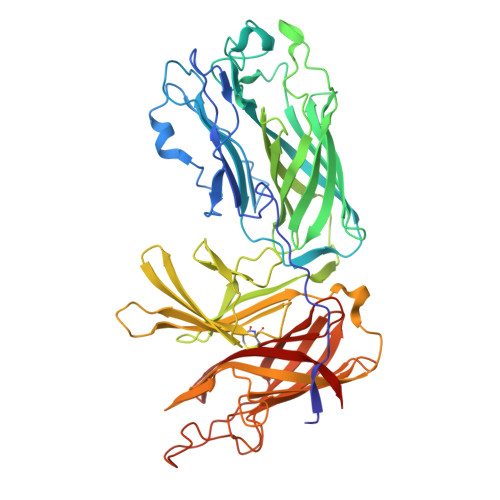
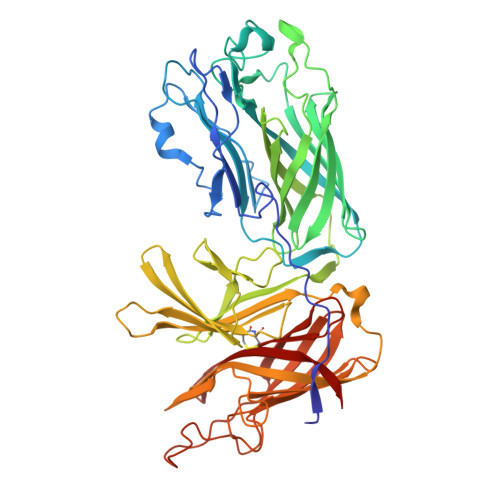
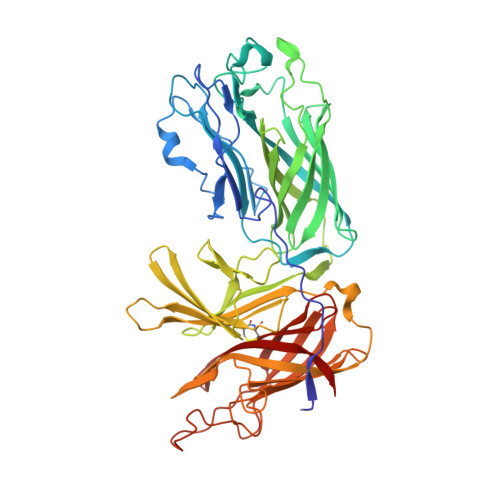
Insights into the bacterial transferrin receptor: the structure of transferrin-binding protein B from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.
Moraes, T.F., Yu, R.H., Strynadka, N.C., Schryvers, A.B.(2009) Mol Cell 35: 523-533
- PubMed: 19716795
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.029
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HOE, 3HOL - PubMed Abstract:
Pathogenic bacteria from the Neisseriaceae and Pasteurellacea families acquire iron directly from the host iron-binding glycoprotein, transferrin (Tf), in a process mediated by surface receptor proteins that directly bind host Tf, extract the iron, and transport it across the outer membrane. The bacterial Tf receptor is comprised of a surface exposed lipoprotein, Tf-binding protein B (TbpB), and an integral outer-membrane protein, Tf-binding protein A (TbpA), both of which are essential for survival in the host. In this study, we report the 1.98 A resolution structure of TbpB from the porcine pathogen Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, providing insights into the mechanism of Tf binding and the role of TbpB. A model for the complex of TbpB bound to Tf is proposed. Mutation of a single surface-exposed Phe residue on TbpB within the predicted interface completely abolishes binding to Tf, suggesting that the TbpB N lobe comprises the sole high-affinity binding region for Tf.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Center for Blood Research, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z3, Canada.