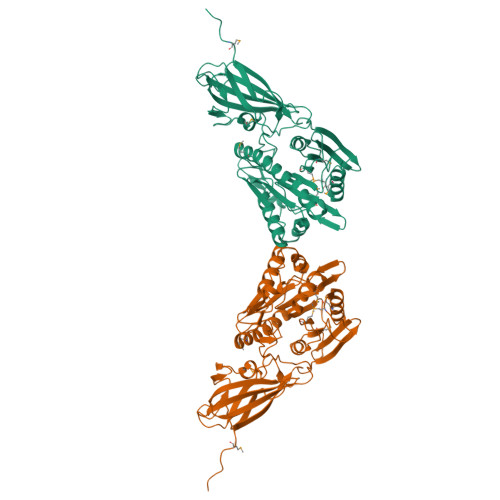
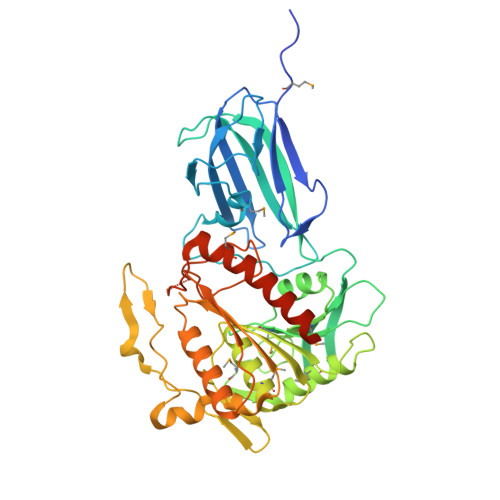
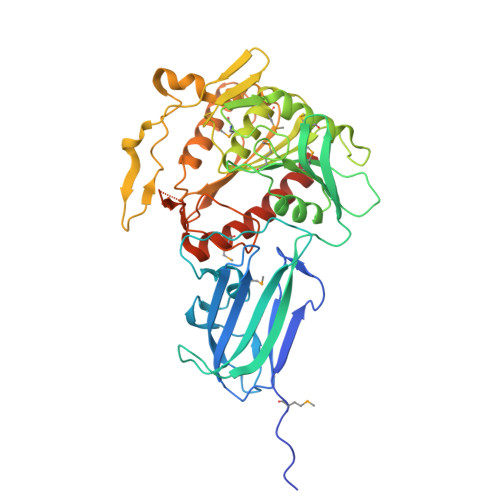
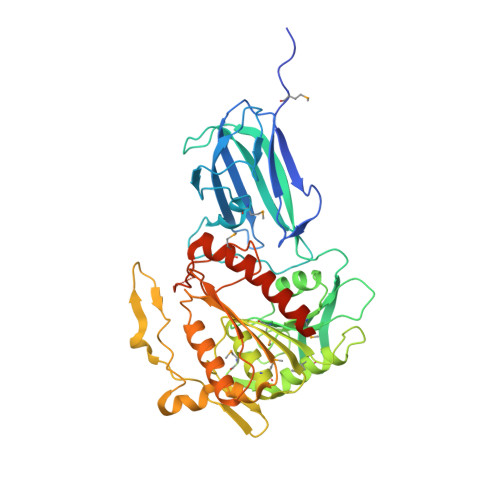
Crystal structure of human mitochondrial acyl-CoA thioesterase (ACOT2)
Mandel, C.R., Tweel, B., Tong, L.(2009) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385: 630-633
- PubMed: 19497300
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.122
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HLK - PubMed Abstract:
Acyl-CoA thioesterases (ACOTs) catalyze the hydrolysis of CoA esters to free CoA and carboxylic acids and have important functions in lipid metabolism and other cellular processes. Type I ACOTs are found only in animals and contain an alpha/beta hydrolase domain, through currently no structural information is available on any of these enzymes. We report here the crystal structure at 2.1A resolution of human mitochondrial ACOT2, a type I enzyme. The structure contains two domains, N and C domains. The C domain has the alpha/beta hydrolase fold, with the catalytic triad Ser294-His422-Asp388. The N domain contains a seven-stranded beta-sandwich, which has some distant structural homologs in other proteins. The active site is located in a large pocket at the interface between the two domains. The structural information has significant relevance for other type I ACOTs and related enzymes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Sciences, Columbia University, New York, NY 10027, USA.