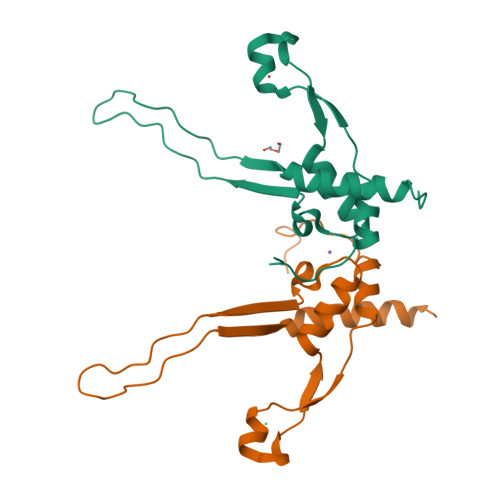
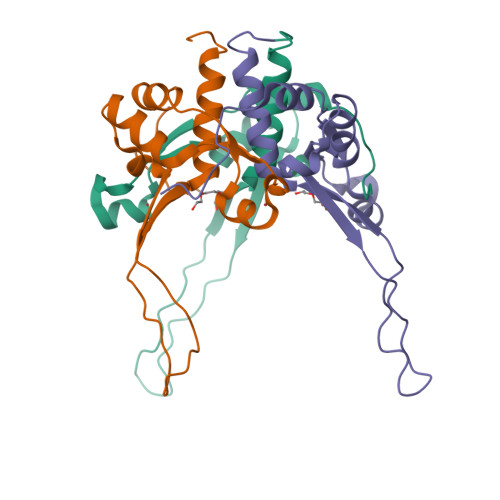
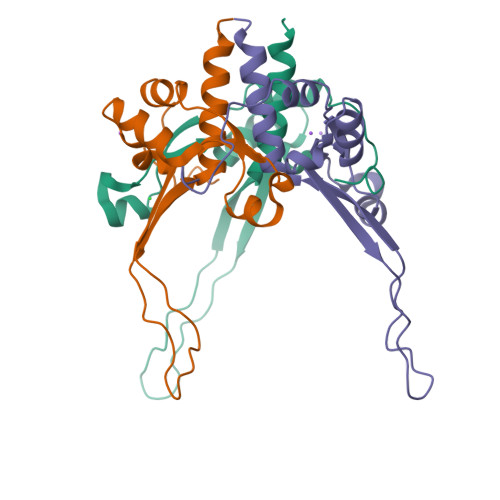
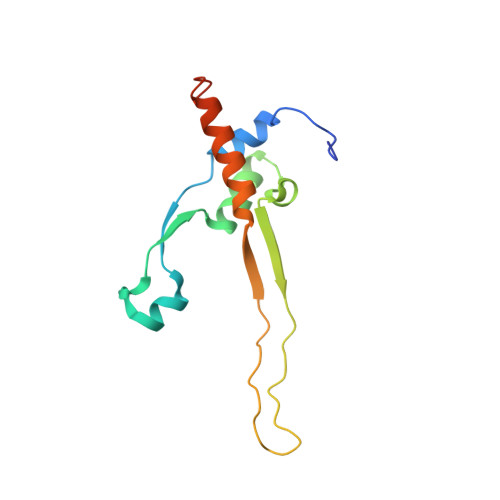
Crystal structure of an intramolecular chaperone mediating triple-beta-helix folding.
Schulz, E.C., Dickmanns, A., Urlaub, H., Schmitt, A., Muhlenhoff, M., Stummeyer, K., Schwarzer, D., Gerardy-Schahn, R., Ficner, R.(2010) Nat Struct Mol Biol 17: 210-215
- PubMed: 20118935
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1746
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GUD, 3GW6 - PubMed Abstract:
Protein folding is often mediated by molecular chaperones. Recently, a novel class of intramolecular chaperones has been identified in tailspike proteins of evolutionarily distant viruses, which require a C-terminal chaperone for correct folding. The highly homologous chaperone domains are interchangeable between pre-proteins and release themselves after protein folding. Here we report the crystal structures of two intramolecular chaperone domains in either the released or the pre-cleaved form, revealing the role of the chaperone domain in the formation of a triple-beta-helix fold. Tentacle-like protrusions enclose the polypeptide chains of the pre-protein during the folding process. After the assembly, a sensory mechanism for correctly folded beta-helices triggers a serine-lysine catalytic dyad to autoproteolytically release the mature protein. Sequence analysis shows a conservation of the intramolecular chaperones in functionally unrelated proteins sharing beta-helices as a common structural motif.
Organizational Affiliation:
Abteilung für Molekulare Strukturbiologie, Institut für Mikrobiologie und Genetik, Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany.