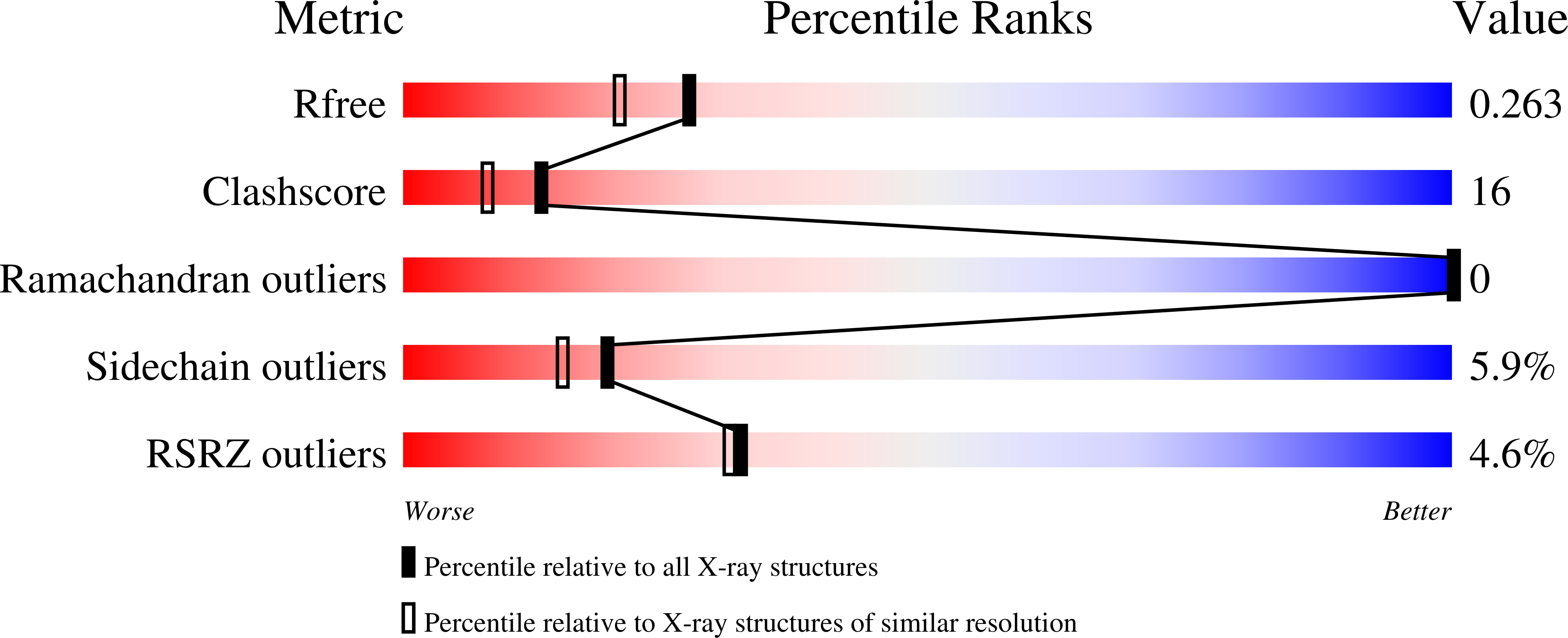
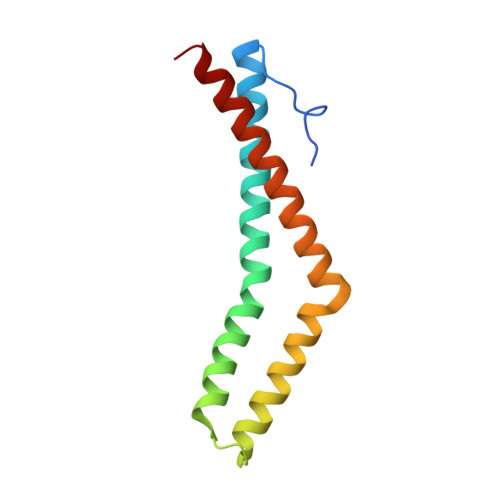
Identification and analysis of occludin phosphosites: a combined mass spectrometry and bioinformatics approach.
Sundstrom, J.M., Tash, B.R., Murakami, T., Flanagan, J.M., Bewley, M.C., Stanley, B.A., Gonsar, K.B., Antonetti, D.A.(2009) J Proteome Res 8: 808-817
- PubMed: 19125584
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/pr7007913
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3G7C - PubMed Abstract:
The molecular function of occludin, an integral membrane component of tight junctions, remains unclear. VEGF-induced phosphorylation sites were mapped on occludin by combining MS data analysis with bioinformatics. In vivo phosphorylation of Ser490 was validated and protein interaction studies combined with crystal structure analysis suggest that Ser490 phosphorylation attenuates the interaction between occludin and ZO-1. This study demonstrates that combining MS data and bioinformatics can successfully identify novel phosphorylation sites from limiting samples.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology, Penn State University College of Medicine, Hershey, Pennsylvania 17033, USA.