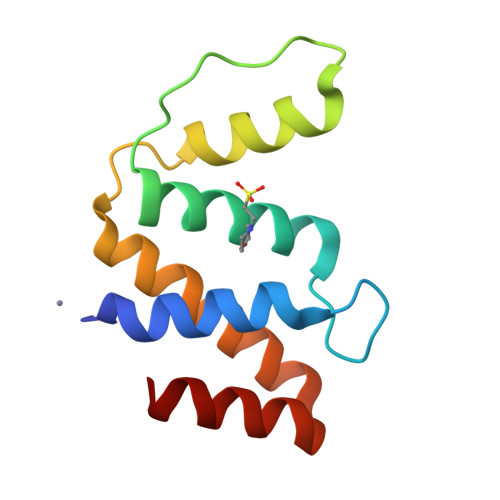
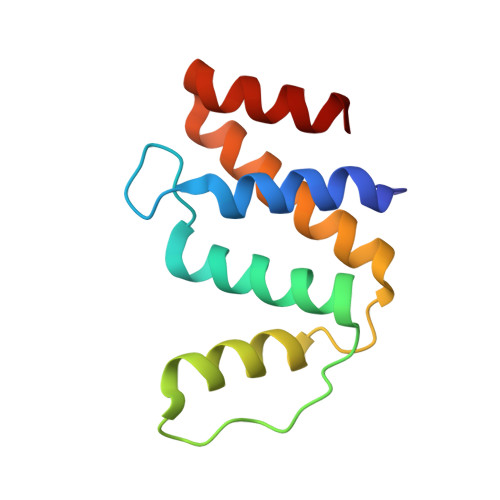
A new topology of ACBP from Moniliophthora perniciosa.
Monzani, P.S., Pereira, H.M., Melo, F.A., Meirelles, F.V., Oliva, G., Cascardo, J.C.(2010) Biochim Biophys Acta 1804: 115-123
- PubMed: 19782157
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.09.020
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3FP5 - PubMed Abstract:
Acyl-CoA binding protein (ACBP) is a housekeeping protein and is an essential protein in human cell lines and in Trypanosoma brucei. The ACBP of Moniliophthora perniciosa is composed of 104 amino acids and is possibly a non-classic isoform exclusively from Basidiomycetes. The M. perniciosa acbp gene was cloned, and the protein was expressed and purified. Acyl-CoA ester binding was analyzed by isoelectric focusing, native gel electrophoresis and isothermal titration calorimetry. Our results suggest an increasing affinity of ACBP for longer acyl-CoA esters, such as myristoyl-CoA to arachidoyl-CoA, and best fit modeling indicates two binding sites. ACBP undergoes a shift from a monomeric to a dimeric state, as shown by dynamic light scattering, fluorescence anisotropy and native gel electrophoresis in the absence and presence of the ligand. The protein's structure was determined at 1.6 A resolution and revealed a new topology for ACBP, containing five alpha-helices instead of four. alpha-helices 1, 2, 3 and 4 adopted a bundled arrangement that is unique from the previously determined four-helix folds of ACBP, while alpha-helices 1, 2, 4 and 5 formed a classical four-helix bundle. A MES molecule was found in the CoA binding site, suggesting that the CoA site could be a target for small compound screening.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departamento de Ciências Biológicas, Laboratório de Proteômica, Centro de Biotecnologia e Genética, Universidade Estadual de Santa Cruz, Ilhéus, BA, CEP 45662-900, Brazil.