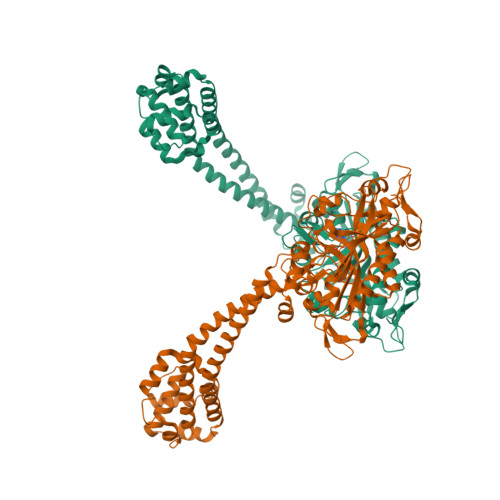
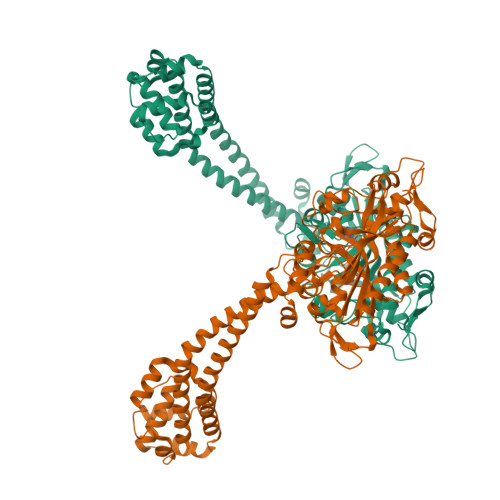
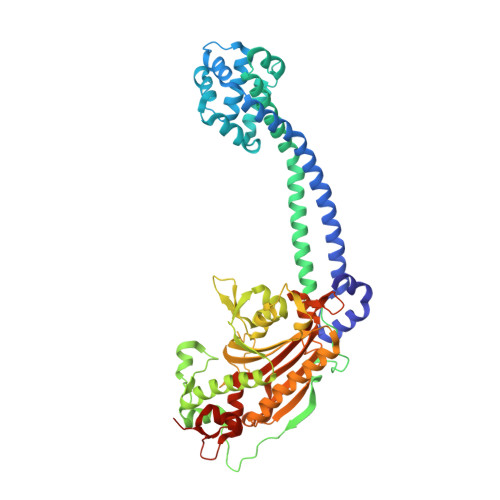
Structure and functional role of dynein's microtubule-binding domain.
Carter, A.P., Garbarino, J.E., Wilson-Kubalek, E.M., Shipley, W.E., Cho, C., Milligan, R.A., Vale, R.D., Gibbons, I.R.(2008) Science 322: 1691-1695
- PubMed: 19074350
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1164424
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ERR - PubMed Abstract:
Dynein motors move various cargos along microtubules within the cytoplasm and power the beating of cilia and flagella. An unusual feature of dynein is that its microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) is separated from its ring-shaped AAA+ adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) domain by a 15-nanometer coiled-coil stalk. We report the crystal structure of the mouse cytoplasmic dynein MTBD and a portion of the coiled coil, which supports a mechanism by which the ATPase domain and MTBD may communicate through a shift in the heptad registry of the coiled coil. Surprisingly, functional data suggest that the MTBD, and not the ATPase domain, is the main determinant of the direction of dynein motility.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology, University of California, San Francisco, CA 94158, USA.