Structural Investigation of the Binding of 5-Substituted Swainsonine Analogues to Golgi alpha-Mannosidase II.
Kuntz, D.A., Nakayama, S., Shea, K., Hori, H., Uto, Y., Nagasawa, H., Rose, D.R.(2010) Chembiochem 11: 673-680
- PubMed: 20209559
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200900750
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3EJP, 3EJQ, 3EJR, 3EJS, 3EJT, 3EJU - PubMed Abstract:
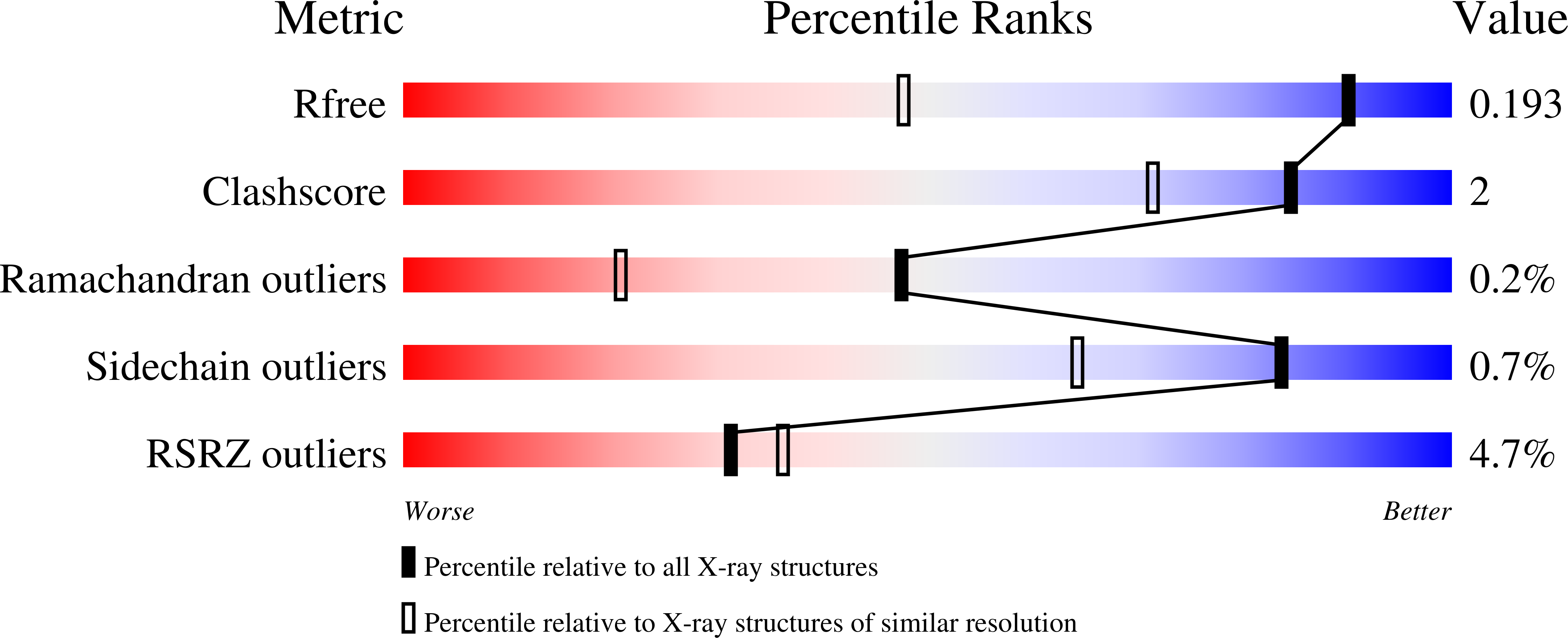
Golgi alpha-mannosidase II (GMII) is a key enzyme in the N-glycosylation pathway and is a potential target for cancer chemotherapy. The natural product swainsonine is a potent inhibitor of GMII. In this paper we characterize the binding of 5alpha-substituted swainsonine analogues to the soluble catalytic domain of Drosophila GMII by X-ray crystallography. These inhibitors enjoy an advantage over previously reported GMII inhibitors in that they did not significantly decrease the inhibitory potential of the swainsonine head-group. The phenyl groups of these analogues occupy a portion of the binding site not previously seen to be populated with either substrate analogues or other inhibitors and they form novel hydrophobic interactions. They displace a well-organized water cluster, but the presence of a C(10) carbonyl allows the reestablishment of important hydrogen bonds. Already approximately tenfold more active against the Golgi enzyme than the lysosomal enzyme, these inhibitors offer the potential of being extended into the N-acetylglucosamine binding site of GMII for the creation of even more potent and selective GMII inhibitors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Ontario Cancer Institute and Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, 101 College Street, Toronto, Ontario, M5G 1L7, Canada.