The First Crystal Structure of Gluconolactonase Important in the Glucose Secondary Metabolic Pathways
Chen, C.-N., Chin, K.-H., Wang, A.H.-J., Chou, S.-H.(2008) J Mol Biol 384: 604-614
- PubMed: 18848569
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.09.055
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DR2 - PubMed Abstract:
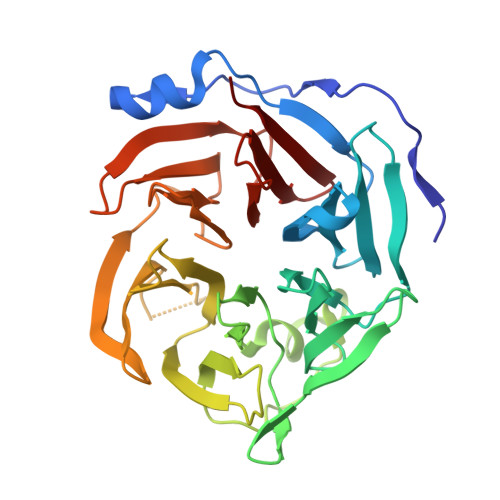
The first gluconolactonase crystal structure from bacteria has been determined to a resolution of 1.61 A using X-ray crystallography. It belongs to the senescence marker protein 30/gluconolaconase superfamily but exhibits substrate specificity mainly toward D-glucono-delta-lactone. It forms a novel disulfide-bonded clamshell dimer comprising two doughnut-shaped six-bladed beta-propeller domains, yet with an exceptionally long N-terminal subdomain forming an extra helix and four additional beta-strands to enclose half of the outermost beta-strands of each propeller. Extensive interactions, including H-bonds, salt bridges, disulfide bonds, and coordination bonds, along with numerous bridging water molecules, are present in the interface to institute the "top-to-top" clamshell-type dimer. Three calcium ions per subunit were observed. Two are present in the central water-filled channel, with the top one coordinated to four highly conserved amino acids and is possibly involved in substrate hydrolysis, while the bottom one is coordinated to the backbone oxygen atoms, which is possibly for stabilizing the propeller domain. One calcium ion is situated in the interface also to stabilize the dimer form. Since gluconolactonase is essential in the glucose secondary metabolic pathways leading to the synthesis of pentose, vitamin C, or "antiaging" factors, determination of its tertiary structure should help understand these important biochemical processes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemistry, National Chung-Hsing University, Taichung 40227, Taiwan, ROC.