Substrate binding of a GH5 endoglucanase from the ruminal fungus Piromyces rhizinflata.
Tseng, C.-W., Ko, T.-P., Guo, R.-T., Huang, J.-W., Wang, H.-C., Huang, C.-H., Cheng, Y.-S., Wang, A.H.-J., Liu, J.-R.(2011) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67: 1189-1194
- PubMed: 22102024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309111032428
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3AYR, 3AYS - PubMed Abstract:
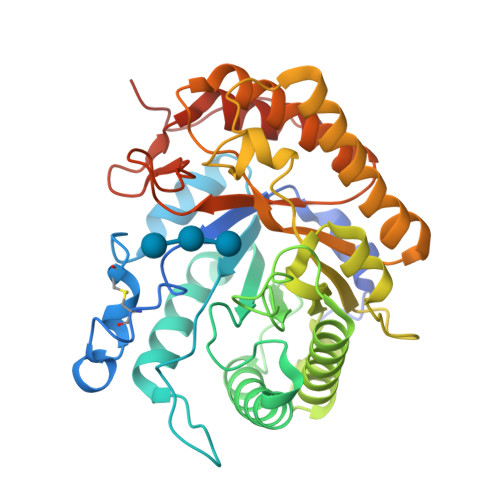
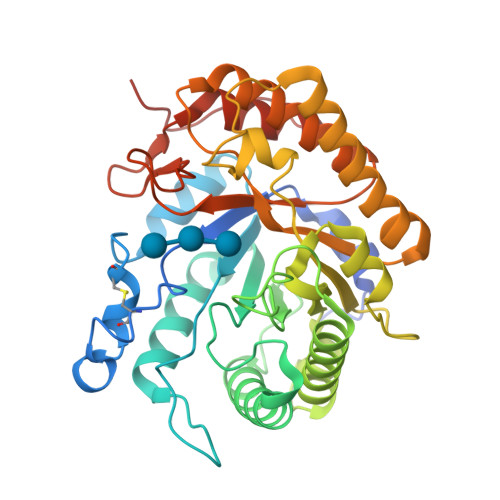
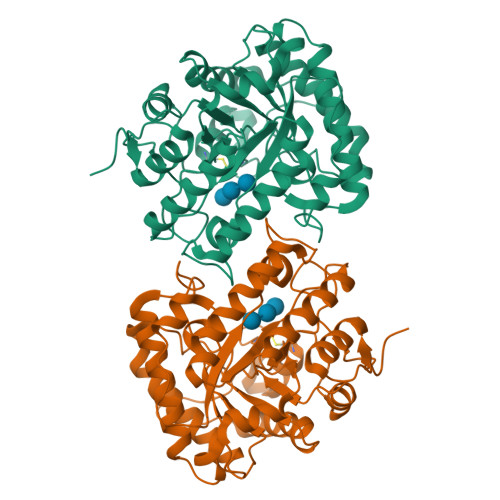
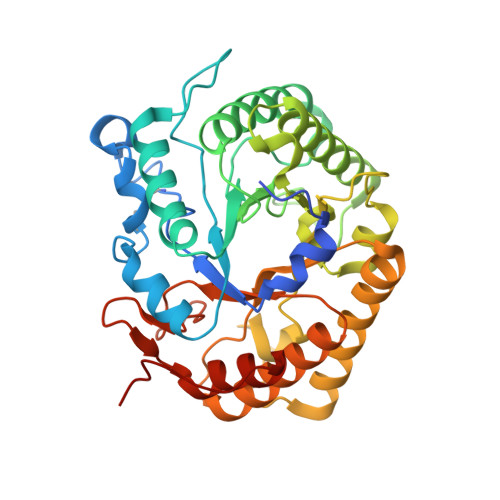
The endoglucanase EglA from Piromyces rhizinflata found in cattle stomach belongs to the GH5 family of glycoside hydrolases. The crystal structure of the catalytic domain of EglA shows the (β/α)(8)-barrel fold typical of GH5 enzymes. Adjacent to the active site of EglA, a loop containing a disulfide bond not found in other similar structures may participate in substrate binding. Because the active site was blocked by the N-terminal His tag of a neighbouring protein molecule in the crystal, enzyme-substrate complexes could not be obtained by soaking but were prepared by cocrystallization. The E154A mutant structure with a cellotriose bound to the -3, -2 and -1 subsites shows an extensive hydrogen-bonding network between the enzyme and the substrate, along with a stacking interaction between Trp44 and the -3 sugar. A possible dimer was observed in the crystal structure, but retention of activity in the E242A mutant suggested that the enzyme probably does not function as a dimer in solution. On the other hand, the first 100 amino acids encoded by the original cDNA fragment are very similar to those in the last third of the (β/α)(8)-barrel fold, indicating that EglA comprises at least two catalytic domains acting in tandem.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biotechnology, National Taiwan University, Taipei 10617, Taiwan.