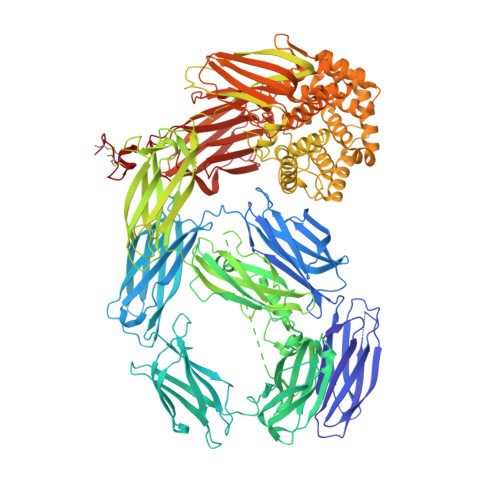
Structural basis for conserved complement factor-like function in the antimalarial protein TEP1
Baxter, R.H.G., Chang, C.I., Chelliah, Y., Blandin, S., Levashina, E.A., Deisenhofer, J.(2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 11615-11620
- PubMed: 17606907
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0704967104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PN5 - PubMed Abstract:
Thioester-containing proteins (TEPs) are a major component of the innate immune response of insects to invasion by bacteria and protozoa. TEPs form a distinct clade of a superfamily that includes the pan-protease inhibitors alpha(2)-macroglobulins and vertebrate complement factors. The essential feature of these proteins is a sequestered thioester bond that, after cleavage in a protease-sensitive region of the protein, is activated and covalently binds to its target. Recently, TEP1 from the malarial vector Anopheles gambiae was shown to mediate recognition and killing of ookinetes from the malarial parasite Plasmodium berghei, a model for the human malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Here, we present the crystal structure of the TEP1 isoform TEP1r. Although the overall protein fold of TEP1r resembles that of complement factor C3, the TEP1r domains are repositioned to stabilize the inactive conformation of the molecule (containing an intact thioester) in the absence of the anaphylotoxin domain, a central component of complement factors. The structure of TEP1r provides a molecular basis for the differences between TEP1 alleles TEP1r and TEP1s, which correlate with resistance of A. gambiae to infection by P. berghei.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, 6001 Forest Park Road, Dallas, TX 75390-9050, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: