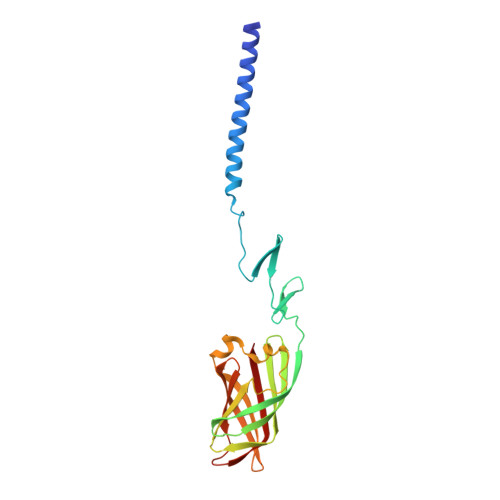
Crystallographic structure of the alpha-helical triple coiled-coil domain of avian reovirus S1133 fibre.
Guardado-Calvo, P., Fox, G.C., Llamas-Saiz, A.L., van Raaij, M.J.(2009) J Gen Virol 90: 672-677
- PubMed: 19218213
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1099/vir.0.008276-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JJL, 2VRS - PubMed Abstract:
Avian reovirus fibre, a homo-trimer of the sigmaC protein, is a minor component of the avian reovirus outer capsid. It is anchored via a short N-terminal sequence to the inner capsid lambdaC pentamer, and its protruding globular C-terminal domain is responsible for primary host cell attachment. We have previously solved the structure of a receptor-binding fragment in which residues 160-191 form a triple beta-spiral and 196-326 a beta-barrel head domain. Here we have expressed, purified and crystallized a major sigmaC fragment comprising residues 117-326. Its structure, which was solved by molecular replacement using the previously determined receptor-binding domain structure and refined to 1.75 A (0.175 nm) resolution, reveals an alpha-helical triple coiled-coil connected to the previously solved structure by a zinc-ion-containing linker. The coiled-coil domain contains two chloride ion binding sites, as well as specific trimerization and registration sequences. The linker may act as a functionally important hinge.
- Departamento de Bioquímica e Bioloxía Molecular, Facultade de Farmacia, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, E-15782 Santiago de Compostela, Spain.
Organizational Affiliation: