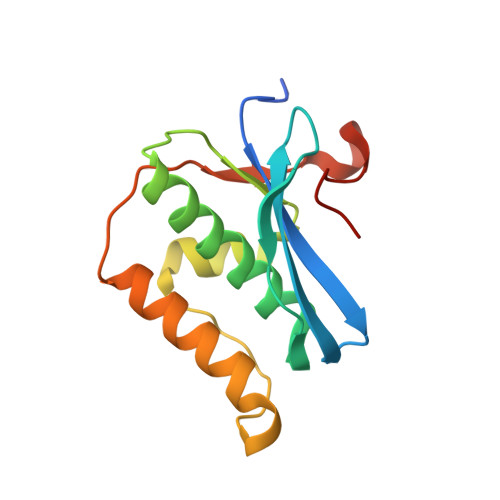
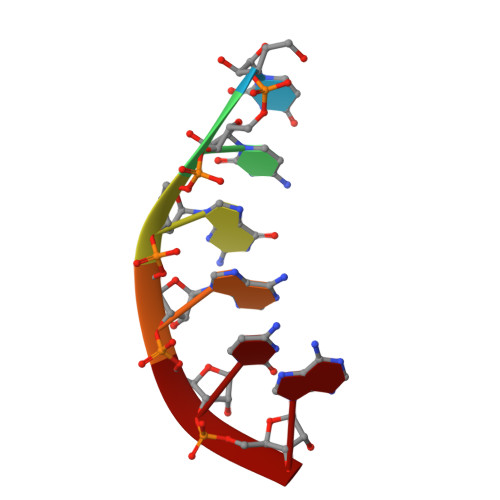
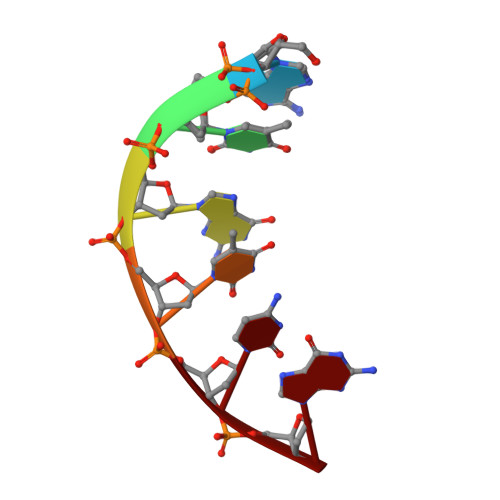
Stepwise analyses of metal ions in RNase H catalysis from substrate destabilization to product release.
Nowotny, M., Yang, W.(2006) EMBO J 25: 1924-1933
- PubMed: 16601679
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601076
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2G8F, 2G8H, 2G8I, 2G8K, 2G8U, 2G8V, 2G8W - PubMed Abstract:
In two-metal catalysis, metal ion A has been proposed to activate the nucleophile and metal ion B to stabilize the transition state. We recently reported crystal structures of RNase H-RNA/DNA substrate complexes obtained at 1.5-2.2 Angstroms. We have now determined and report here structures of reaction intermediate and product complexes of RNase H at 1.65-1.85 Angstroms. The movement of the two metal ions suggests how they may facilitate RNA hydrolysis during the catalytic process. Firstly, metal ion A may assist nucleophilic attack by moving towards metal ion B and bringing the nucleophile close to the scissile phosphate. Secondly, metal ion B transforms from an irregular coordination in the substrate complex to a more regular geometry in the product complex. The exquisite sensitivity of Mg(2+) to the coordination environment likely destabilizes the enzyme-substrate complex and reduces the energy barrier to form product. Lastly, product release probably requires dissociation of metal ion A, which is inhibited by either high concentrations of divalent cations or mutation of an assisting protein residue.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: