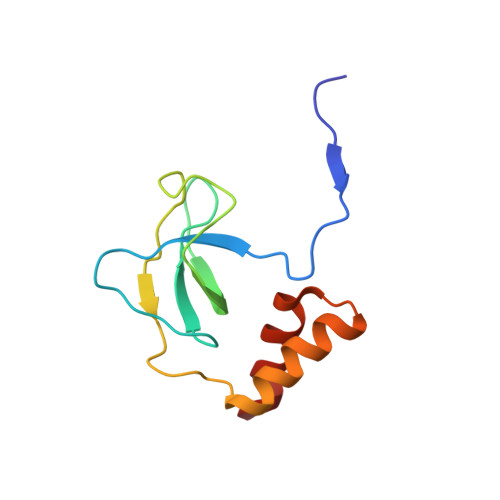
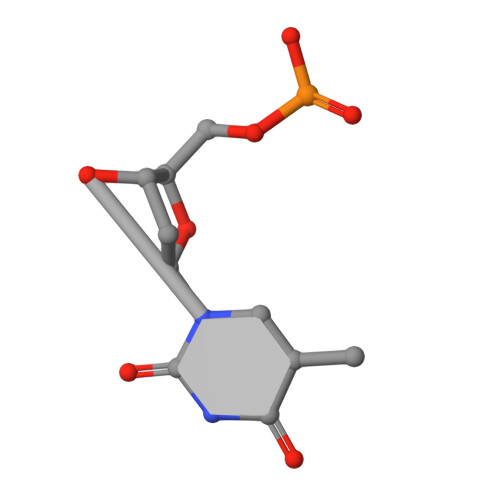
Structural basis of the 3'-end recognition of a leading strand in stalled replication forks by PriA.
Sasaki, K., Ose, T., Okamoto, N., Maenaka, K., Tanaka, T., Masai, H., Saito, M., Shirai, T., Kohda, D.(2007) EMBO J 26: 2584-2593
- PubMed: 17464287
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601697
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2D7E, 2D7G, 2D7H, 2DWL, 2DWM, 2DWN - PubMed Abstract:
In eubacteria, PriA helicase detects the stalled DNA replication forks. This critical role of PriA is ascribed to its ability to bind to the 3' end of a nascent leading DNA strand in the stalled replication forks. The crystal structures in complexes with oligonucleotides and the combination of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and mutagenesis reveal that the N-terminal domain of PriA possesses a binding pocket for the 3'-terminal nucleotide residue of DNA. The interaction with the deoxyribose 3'-OH is essential for the 3'-terminal recognition. In contrast, the direct interaction with 3'-end nucleobase is unexpected, considering the same affinity for oligonucleotides carrying the four bases at the 3' end. Thus, the N-terminal domain of PriA recognizes the 3'-end base in a base-non-selective manner, in addition to the deoxyribose and 5'-side phosphodiester group, of the 3'-terminal nucleotide to acquire both sufficient affinity and non-selectivity to find all of the stalled replication forks generated during DNA duplication. This unique feature is prerequisite for the proper positioning of the helicase domain of PriA on the unreplicated double-stranded DNA.
- Division of Structural Biology, Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: