Structural Basis for Cooperative Transcription Factor Binding to the CBP Coactivator
De Guzman, R.N., Goto, N.K., Dyson, H.J., Wright, P.E.(2006) J Mol Biology 355: 1005-1013
- PubMed: 16253272
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.09.059
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2AGH - PubMed Abstract:
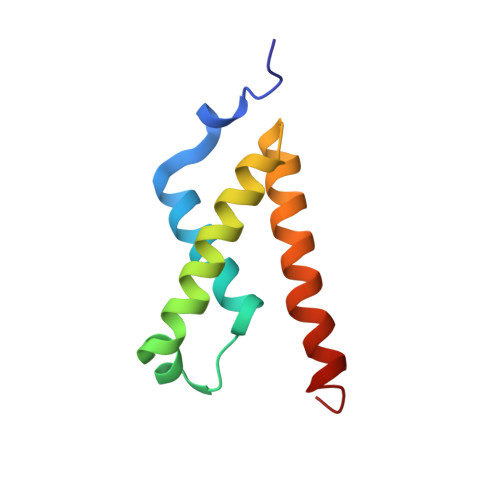
Regulation of transcription requires interactions between transcriptional activators and transcriptional co-activator CREB binding protein (CBP). The KIX domain of CBP can bind simultaneously to two different proteins, providing an additional mechanism for transcriptional regulation. Here we describe the solution structure of the ternary complex formed by cooperative binding of activation domains from the c-Myb and mixed lineage leukemia (MLL) transcription factors to the KIX domain. The MLL and c-Myb domains form helices that bind to two distinct hydrophobic grooves on opposite faces of KIX. Compared to the binary KIX:c-Myb complex, significant changes are observed in the structure of KIX at the MLL binding interface in the ternary complex. Two regions of KIX that are disordered in the binary complex become structured in the ternary complex: a flexible loop forms intimate contacts with bound MLL, and the C-terminal helix is extended and stabilized by MLL binding. This structural change results in the formation of additional electrostatic/polar interactions between KIX and the bound c-Myb, providing a structural basis for the cooperativity observed for the ternary complex.
- Department of Molecular Biology MB2, The Scripps Research Institute 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: