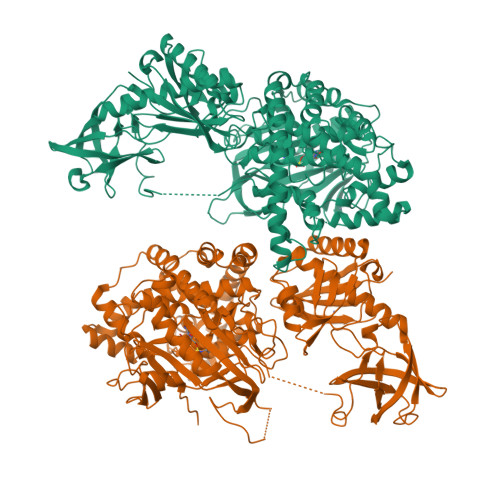
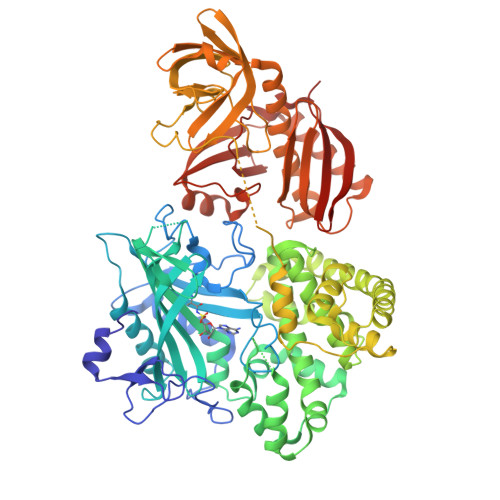
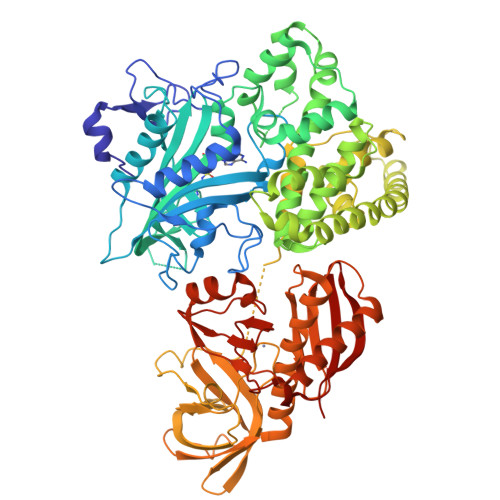
The structure of alanyl-tRNA synthetase with editing domain.
Sokabe, M., Ose, T., Nakamura, A., Tokunaga, K., Nureki, O., Yao, M., Tanaka, I.(2009) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: 11028-11033
- PubMed: 19549823
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904645106
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2ZZE, 2ZZF, 2ZZG - PubMed Abstract:
Alanyl-tRNA synthetase (AlaRS) catalyzes synthesis of Ala-tRNA(Ala) and hydrolysis of mis-acylated Ser- and Gly-tRNA(Ala) at 2 different catalytic sites. Here, we describe the monomer structures of C-terminal truncated archaeal AlaRS, with both activation and editing domains in the apo form, in complex with an Ala-AMP analog, and in a high-resolution lysine-methylated form. The structures show docking of the editing domain to the activation domain opposite from the predicted tRNA-binding surface. Thus, the editing site is positioned >35 A from the activation site, prompting us to model 2 different tRNA complexes: one binding tRNA at the activation site, and the other binding tRNA at the editing site. Interestingly, a gel-shift assay also implies the presence of 2 types of tRNA complex with different mobility. These results suggest that tRNA translocation via a canonical CCA flipping is unlikely to occur in AlaRS. The structure also demonstrated the binding of zinc in the editing site, in which the specific coordination of zinc would be facilitated by a conserved GGQ motif, implying that the editing mechanism may not be the same as in ThrRS. As Asn-194 in eubacterial AlaRS important for Ser misactivation is replaced by Thr-213 in archaeal AlaRS, a different Ser accommodation mechanism is proposed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Advanced Life Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 060-0810, Japan.