Molecular Basis for the Selectivity and Specificity of Ligand Recognition by the Family 16 Carbohydrate-binding Modules from Thermoanaerobacterium polysaccharolyticum ManA
Bae, B., Ohene-Adjei, S., Kocherginskaya, S., Mackie, R.I., Spies, M.A., Cann, I.K., Nair, S.K.(2008) J Biological Chem 283: 12415-12425
- PubMed: 18025086
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M706513200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2ZEW, 2ZEX, 2ZEY, 2ZEZ - PubMed Abstract:
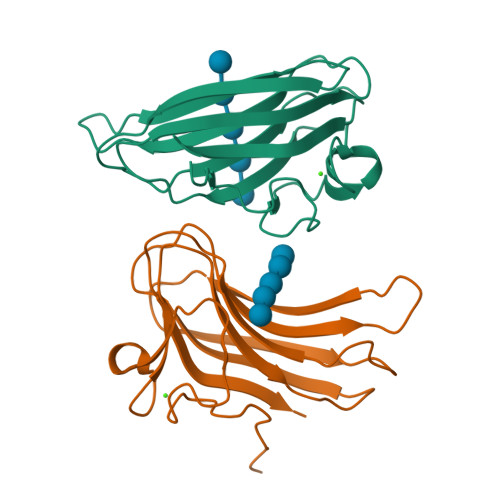
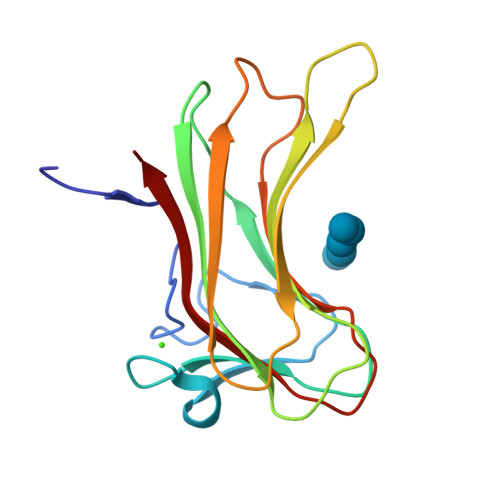
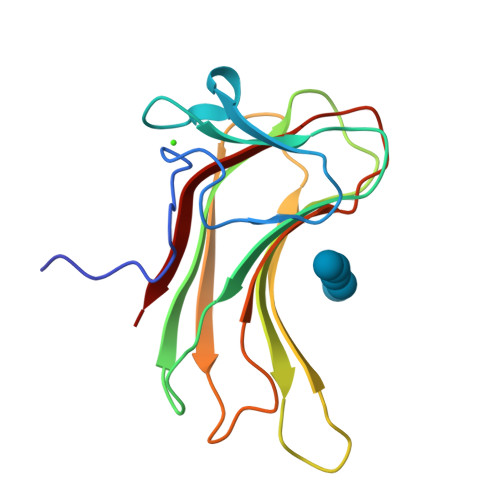
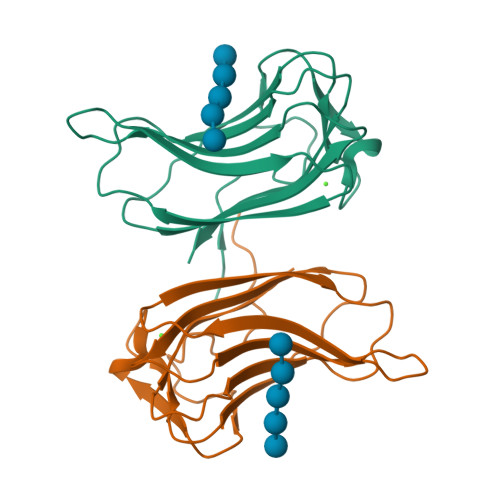
Enzymes that hydrolyze complex polysaccharides into simple sugars are modular in architecture and consist of single or multiple catalytic domains fused to targeting modules called carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs). CBMs bind to their ligands with high affinity and increase the efficiency of the catalytic components by targeting the enzymes to its substrate. Here we utilized a multidisciplinary approach to characterize each of the two family 16 carbohydrate-binding domain components of the highly active mannanase from the thermophile Thermoanaerobacterium polysaccharolyticum. These represent the first crystal structures of family 16 CBMs. Calorimetric analysis showed that although these CBMs demonstrate high specificity toward beta-1,4-linked sugars, they can engage both cello- and mannopolysaccharides. To elucidate the molecular basis for this specificity and selectivity, we have determined high resolution crystal structures of each of the two CBMs, as well as of binary complexes of CBM16-1 bound to either mannopentaose or cellopentaose. These results provide detailed molecular insights into ligand recognition and yield a framework for rational engineering experiments designed to expand the natural repertoire of these targeting modules.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, Illinois 61801, USA.