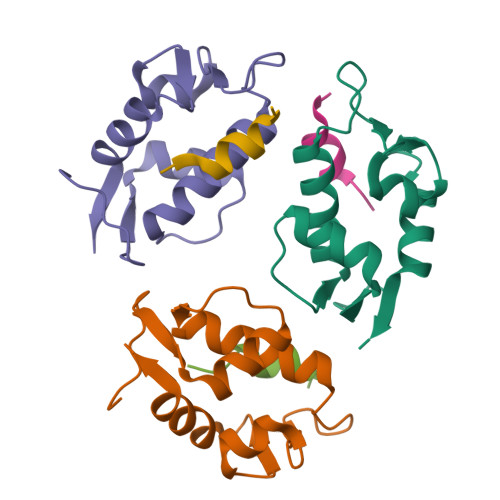
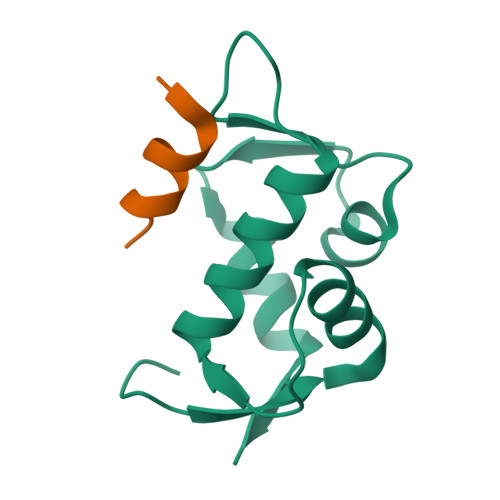
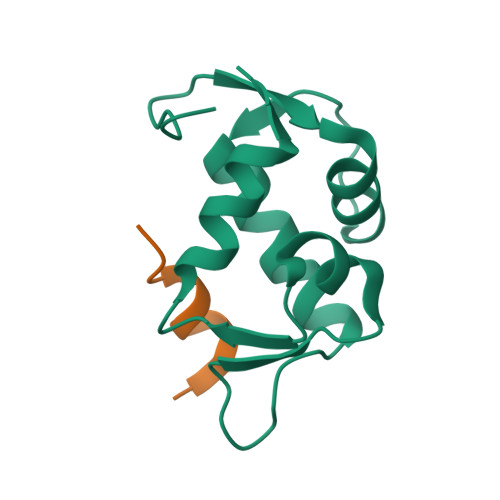
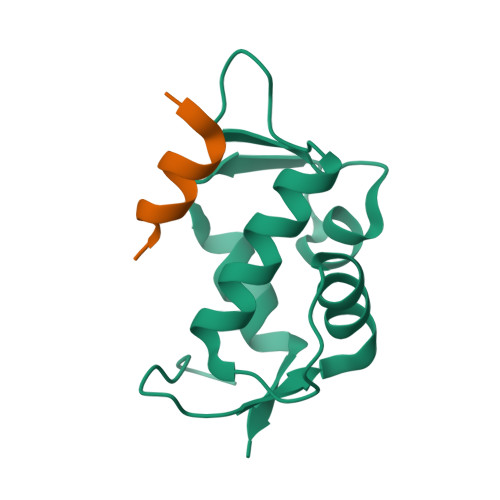
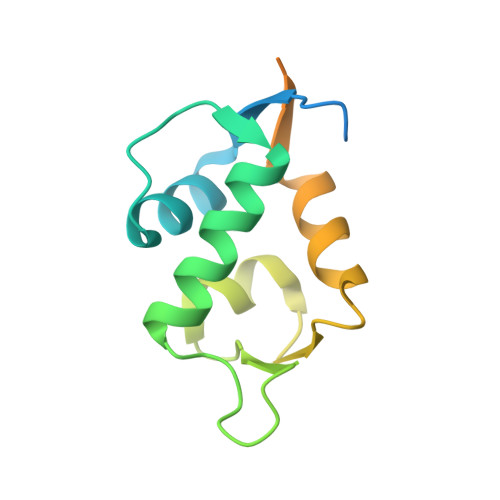
Molecular basis for the inhibition of p53 by Mdmx.
Popowicz, G.M., Czarna, A., Rothweiler, U., Szwagierczak, A., Krajewski, M., Weber, L., Holak, T.A.(2007) Cell Cycle 6: 2386-2392
- PubMed: 17938582
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.6.19.4740
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2Z5S, 2Z5T - PubMed Abstract:
The oncoprotein Mdm2, and the recently intensely studied, homologues protein Mdmx, are principal negative regulators of the p53 tumor suppressor. The mechanisms by which they regulate the stability and activity of p53 are not fully established. We have determined the crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of Mdmx bound to a 15-residue p53 peptide. The structure reveals that although the principle features of the Mdm2-p53 interaction are preserved in the Mdmx-p53 complex, the Mdmx hydrophobic cleft on which the p53 peptide binds is significantly altered: a part of the cleft is blocked by sidechains of Met and Tyr of the p53-binding pocket of Mdmx. Thus specific inhibitors of Mdm2-p53 would not be optimal for binding to Mdmx. Our binding assays show indeed that nutlins, the newly discovered, potent antagonists of the Mdm2-p53 interaction, are not capable to efficiently disrupt the Mdmx-p53 interaction. To achieve full activation of p53 in tumor cells, compounds that are specific for Mdmx are necessary to complement the Mdm2 specific binders.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max Planck Institute for Biochemistry, Martinsried, Germany.