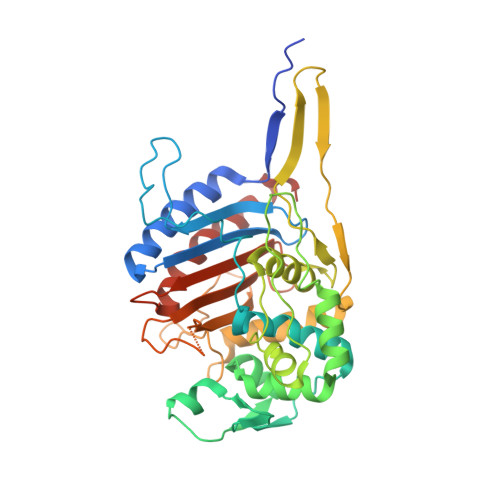
Crystal Structure of Cefditoren Complexed with Streptococcus pneumoniae Penicillin-Binding Protein 2X: Structural Basis for its High Antimicrobial Activity
Yamada, M., Watanabe, T., Miyara, T., Baba, N., Saito, J., Takeuchi, Y., Ohsawa, F.(2007) Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51: 3902-3907
- PubMed: 17724158
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00743-07
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2Z2L, 2Z2M - PubMed Abstract:
Cefditoren is the active form of cefditoren pivoxil, an oral cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of respiratory tract infections and otitis media caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and methicillin-susceptible strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Beta-lactam antibiotics, including cefditoren, target penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), which are membrane-associated enzymes that play essential roles in the peptidoglycan biosynthetic process. To envision the binding of cefditoren to PBPs, we determined the crystal structure of a trypsin-digested form of PBP 2X from S. pneumoniae strain R6 complexed with cefditoren. There are two PBP 2X molecules (designated molecules 1 and 2) per asymmetric unit. The structure reveals that the orientation of Trp374 in each molecule changes in a different way upon the formation of the complex, but each forms a hydrophobic pocket. The methylthiazole group of the C-3 side chain of cefditoren fits into this binding pocket, which consists of residues His394, Trp374, and Thr526 in molecule 1 and residues His394, Asp375, and Thr526 in molecule 2. The formation of the complex is also accompanied by an induced-fit conformational change of the enzyme in the pocket to which the C-7 side chain of cefditoren binds. These features likely play a role in the high level of activity of cefditoren against S. pneumoniae.
Organizational Affiliation:
Pharmaceutical Research Center, Meiji Seika Kaisha, Ltd., 760 Morooka-cho, Kohoku-ku, Yokohama 222-8567, Japan. mototsugu_yamada@meiji.co.jp