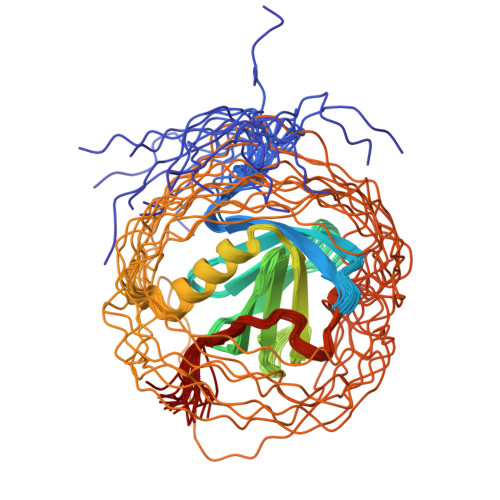
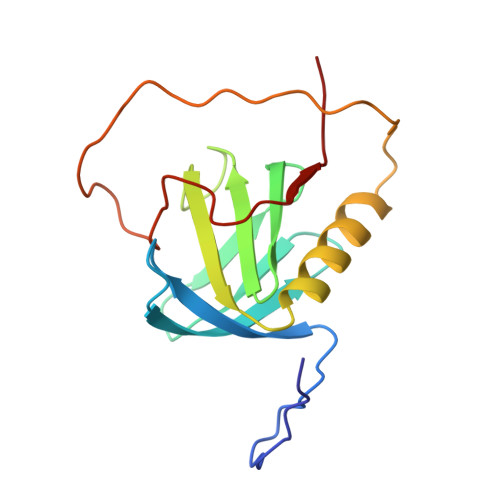
Structural basis for the recognition of nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase oncoprotein by the phosphotyrosine binding domain of Suc1-associated neurotrophic factor-induced tyrosine-phosphorylated target-2
Koshiba, S., Li, H., Motoda, Y., Tomizawa, T., Kasai, T., Tochio, N., Yabuki, T., Harada, T., Watanabe, S., Tanaka, A., Shirouzu, M., Kigawa, T., Yamamoto, T., Yokoyama, S.(2010) J Struct Funct Genomics 11: 125-141
- PubMed: 20454865
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10969-010-9091-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KUP, 2KUQ, 2YS5, 2YT2 - PubMed Abstract:
The nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (NPM-ALK) fusion oncoprotein, formed by the t(2;5) chromosomal translocation in anaplastic large-cell lymphomas, has constitutive tyrosine kinase activity and interacts with a number of signaling molecules. One of the interacting partners of NPM-ALK is the adaptor protein, Suc1-associated neurotrophic factor-induced tyrosine-phosphorylated target (SNT), and mutations that deprive NPM-ALK of all three of the SNT-binding sites significantly reduced the transforming activity. In this study, the interactions of the three binding sites in NPM-ALK with the phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domain of SNT-2 were analyzed. First, by isothermal titration calorimetry, we found that the phosphorylation-independent binding site in NPM-ALK interacts with the SNT-2 PTB domain more tightly than the phosphorylation-dependent binding sites. Second, the solution structure of the SNT-2 PTB domain in complex with the nonphosphorylated NPM-ALK peptide was determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The NPM-ALK peptide interacts with the hydrophobic surface of the PTB domain and intermolecularly extends the PTB beta-sheet. This interaction mode is much broader and more extensive than those of the phosphorylation-dependent binding sites. Our results indicate that the higher binding activity of the phosphorylation-independent binding site is caused by additional hydrophobic interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
RIKEN Systems and Structural Biology Center, 1-7-22 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi, Yokohama 230-0045, Japan.