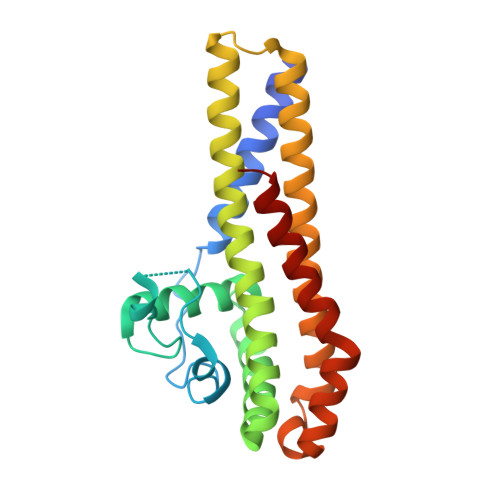
Crystal Structure of the Infectious Phenotype-Associated Outer Surface Protein Bba66 from the Lyme Disease Agent Borrelia Burgdorferi.
Brangulis, K., Petrovskis, I., Kazaks, A., Tars, K., Ranka, R.(2014) Ticks Tick Borne Dis 5: 63
- PubMed: 24246708
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.09.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2YN7 - PubMed Abstract:
Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease is transmitted to the mammalian host organisms by infected Ixodes ticks. Transfer of the spirochaetal bacteria from Ixodes ticks to the warm-blooded mammalian organism provides a challenge for the bacteria to adapt and survive in the different environmental conditions. B. burgdorferi has managed to differentially express genes in response to the encountered changes such as temperature and pH variance or metabolic rate to survive in both environments. In recent years, much interest has been turned on genes that are upregulated during the borrelial transfer to mammalian organisms as this could reveal the proteins important in the pathogenesis of Lyme disease. BBA66 is one of the upregulated outer surface proteins thought to be important in the pathogenesis of B. burgdorferi as it has been found out that BBA66 is necessary during the transmission and propagation phase to initiate Lyme disease. As there is still little known about the pathogenesis of B. burgdorferi, we have solved the crystal structure of the outer surface protein BBA66 at 2.25Å resolution. A monomer of BBA66 consists of 6 α-helices packed in a globular domain, and the overall folding is similar to the homologous proteins BBA64, BBA73, and CspA. Structure-based sequence alignment with the homologous protein BBA64 revealed that the conserved residues are mainly located inwards the core region of the protein and thus may be required to maintain the overall fold of the protein. Unlike the other homologous proteins, BBA66 has an atypically long disordered region at the N terminus thought to act as a "tether" between the structural domain and the cell surface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Latvian Biomedical Research and Study Centre, Ratsupites 1, LV-1067 Riga, Latvia; Riga Stradins University, Dzirciema 16, LV-1007 Riga, Latvia. Electronic address: kalvis@biomed.lu.lv.