Crystal Structure of Enzyme I of the Phosphoenolpyruvate:Sugar Phosphotransferase System in the Dephosphorylated State.
Oberholzer, A.E., Schneider, P., Siebold, C., Baumann, U., Erni, B.(2009) J Biological Chem 284: 33169
- PubMed: 19801641
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.057612
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WQD - PubMed Abstract:
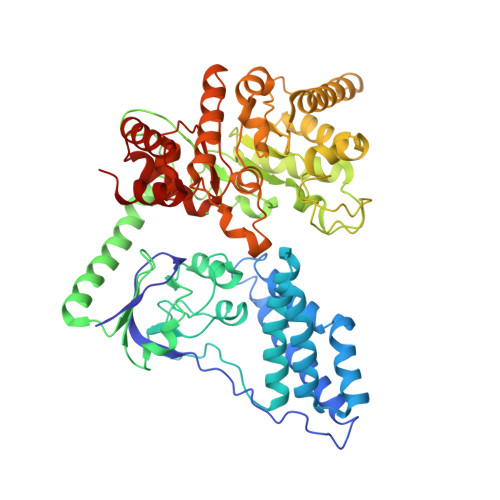
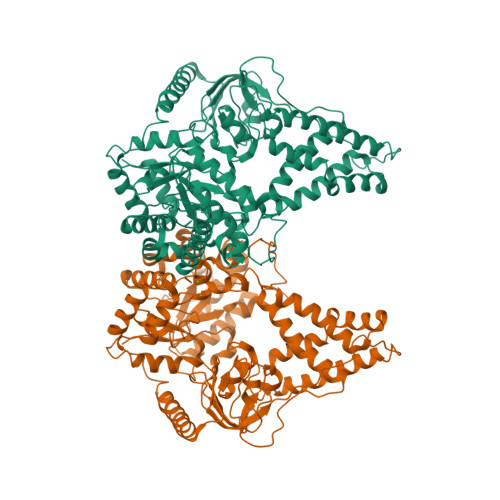
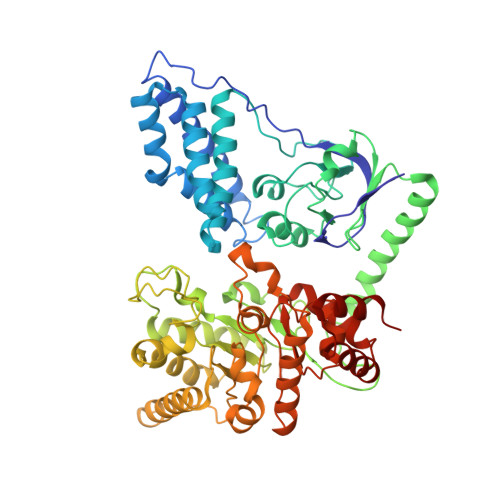
The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) sugar phosphotransferase system mediates sugar uptake and controls the carbon metabolism in response to carbohydrate availability. Enzyme I (EI), the first component of the phosphotransferase system, consists of an N-terminal protein binding domain (EIN) and a C-terminal PEP binding domain (EIC). EI transfers phosphate from PEP by double displacement via a histidine residue on EIN to the general phosphoryl carrier protein HPr. Here we report the 2.4 A crystal structure of the homodimeric EI from Staphylococcus aureus. EIN consists of the helical hairpin HPr binding subdomain and the phosphorylatable betaalpha phospho-histidine (P-His) domain. EIC folds into an (betaalpha)(8) barrel. The dimer interface of EIC buries 1833 A(2) of accessible surface per monomer and contains two Ca(2+) binding sites per dimer. The structures of the S. aureus and Escherichia coli EI domains (Teplyakov, A., Lim, K., Zhu, P. P., Kapadia, G., Chen, C. C., Schwartz, J., Howard, A., Reddy, P. T., Peterkofsky, A., and Herzberg, O. (2006) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 16218-16223) are very similar. The orientation of the domains relative to each other, however, is different. In the present structure the P-His domain is docked to the HPr binding domain in an orientation appropriate for in-line transfer of the phosphate to the active site histidine of the acceptor HPr. In the E. coli structure the phospho-His of the P-His domain projects into the PEP binding site of EIC. In the S. aureus structure the crystallographic temperature factors are lower for the HPr binding domain in contact with the P-His domain and higher for EIC. In the E. coli structure it is the reverse.
Organizational Affiliation:
Departement für Chemie und Biochemie, Universität Bern, Freiestrasse 3, CH-3012 Bern, Switzerland.