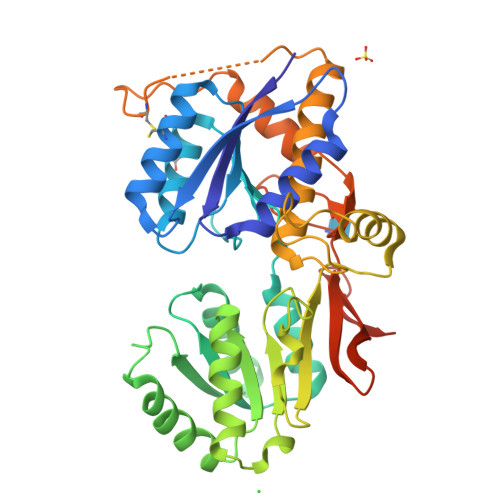
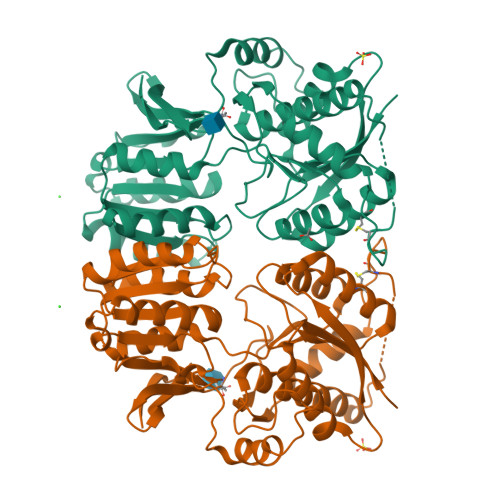
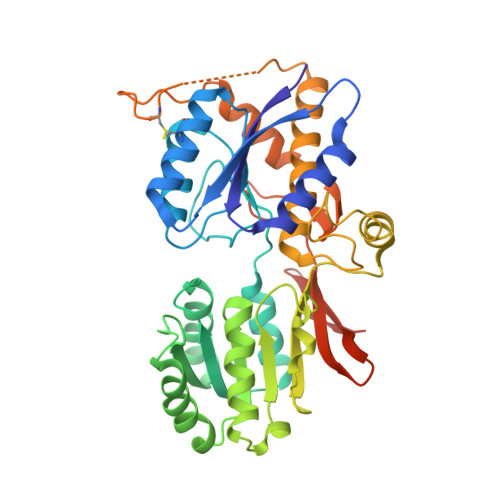
Crystal Structure of the Glur2 Amino-Terminal Domain Provides Insights Into the Architecture and Assembly of Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors.
Clayton, A., Siebold, C., Gilbert, R.J.C., Sutton, G.C., Harlos, K., Mcilhinney, R.A.J., Jones, E.Y., Aricescu, A.R.(2009) J Mol Biology 392: 1125
- PubMed: 19651138
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.07.082
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WJW, 2WJX - PubMed Abstract:
Ionotropic glutamate receptors are functionally diverse but have a common architecture, including the 400-residue amino-terminal domain (ATD). We report a 1.8-A resolution crystal structure of human GluR2-ATD. This dimeric structure provides a mechanism for how the ATDs can drive receptor assembly and subtype-restricted composition. Lattice contacts in a 4.1-A resolution crystal form reveal a tetrameric (dimer-dimer) arrangement consistent with previous cellular and cryo-electron microscopic data for full-length AMPA receptors.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford, Roosevelt Drive, Oxford, UK.