Cysteine Usage in Sulfolobus Spindle-Shaped Virus 1 and Extension to Hyperthermophilic Viruses in General.
Menon, S.K., Maaty, W.S., Corn, G.J., Kwok, S.C., Eilers, B.J., Kraft, P., Gillitzer, E., Young, M.J., Bothner, B., Lawrence, C.M.(2008) Virology 376: 270
- PubMed: 18471851
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2008.03.026
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VQC - PubMed Abstract:
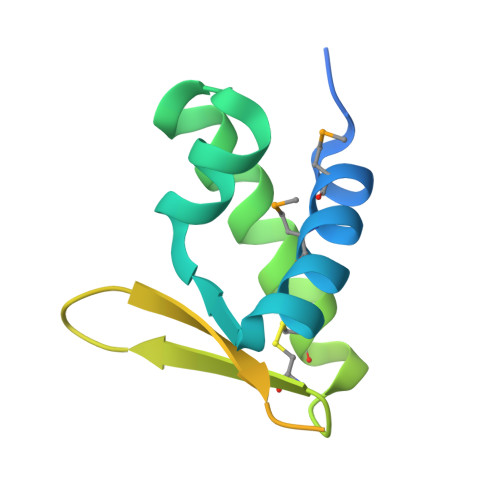
Fuselloviridae are ubiquitous crenarchaeal viruses found in high-temperature acidic hot springs worldwide. The type virus, Sulfolobus spindle-shaped virus 1 (SSV1), has a double-stranded DNA genome that contains 34 open reading frames (ORFs). Fuselloviral genomes show little similarity to other organisms, generally precluding functional predictions. However, tertiary protein structure can provide insight into protein function. We have thus undertaken a systematic investigation of the SSV1 proteome and report here on the F112 gene product. Biochemical, proteomic and structural studies reveal a monomeric intracellular protein that adopts a winged helix DNA binding fold. Notably, the structure contains an intrachain disulfide bond, prompting analysis of cysteine usage in this and other hyperthermophilic viral genomes. The analysis supports a general abundance of disulfide bonds in the intracellular proteins of hyperthermophilic viruses, and reveals decreased cysteine content in the membrane proteins of hyperthermophilic viruses infecting Sulfolobales. The evolutionary implications of the SSV1 distribution are discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
Thermal Biology Institute, Montana State University, Bozeman, MT 59717, USA.