Structure of a Putative Acetyltransferase (Pa1377) from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa.
Davies, A.M., Tata, R., Chauviac, F.X., Sutton, B.J., Brown, P.R.(2008) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 64: 338
- PubMed: 18453699
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309108007665
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VI7 - PubMed Abstract:
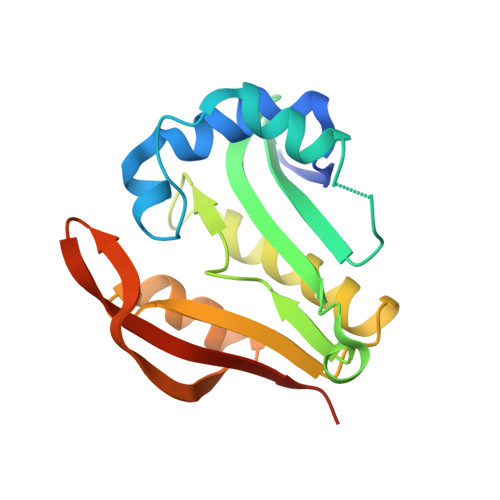
Gene PA1377 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a 177-amino-acid conserved hypothetical protein of unknown function. The structure of this protein (termed pitax) has been solved in space group I222 to 2.25 A resolution. Pitax belongs to the GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase family and contains all four sequence motifs conserved among family members. The beta-strand structure in one of these motifs (motif A) is disrupted, which is believed to affect binding of the substrate that accepts the acetyl group from acetyl-CoA.
Organizational Affiliation:
Randall Division of Cell and Molecular Biophysics, King's College London, New Hunt's House, Guy's Campus, London Bridge, London SE1 1UL, England.