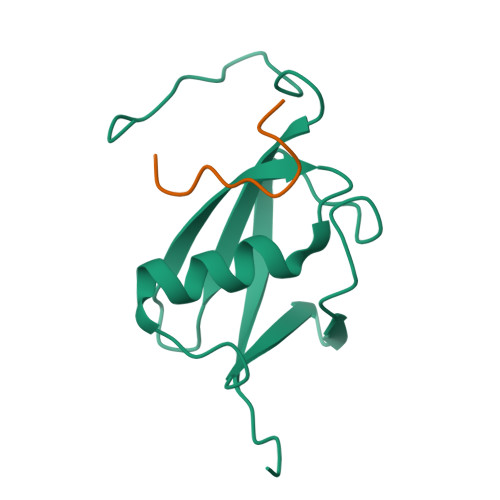
Structure of the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO)-interacting motif of MBD1-containing chromatin-associated factor 1 bound to SUMO-3
Sekiyama, N., Ikegami, T., Yamane, T., Ikeguchi, M., Uchimura, Y., Baba, D., Ariyoshi, M., Tochio, H., Saitoh, H., Shirakawa, M.(2008) J Biological Chem 283: 35966-35975
- PubMed: 18842587
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M802528200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2RPQ - PubMed Abstract:
Post-translational modification by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) proteins has been implicated in the regulation of a variety of cellular events. The functions of sumoylation are often mediated by downstream effector proteins harboring SUMO-interacting motifs (SIMs) that are composed of a hydrophobic core and a stretch of acidic residues. MBD1-containing chromatin-associated factor 1 (MCAF1), a transcription repressor, interacts with SUMO-2/3 and SUMO-1, with a preference for SUMO-2/3. We used NMR spectroscopy to solve the solution structure of the SIM of MCAF1 bound to SUMO-3. The hydrophobic core of the SIM forms a parallel beta-sheet pairing with strand beta2 of SUMO-3, whereas its C-terminal acidic stretch seems to mediate electrostatic interactions with a surface area formed by basic residues of SUMO-3. The significance of these electrostatic interactions was shown by mutations of both SUMO-3 and MCAF1. The present structural and biochemical data suggest that the acidic stretch of the SIM of MCAF1 plays an important role in the binding to SUMO-3.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University, Kyoto 615-8510, Japan.