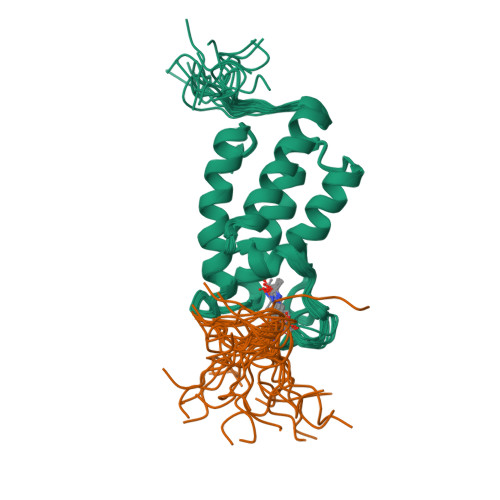
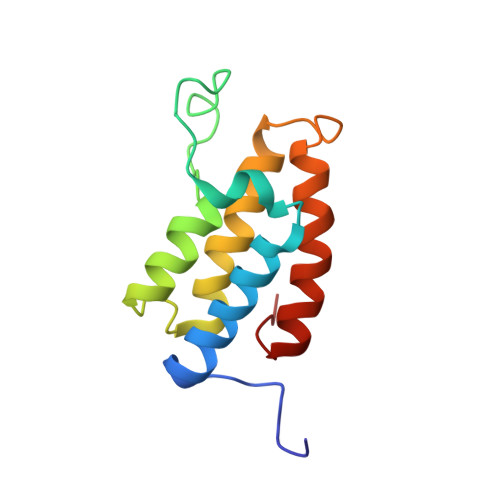
Structural Basis of Site-Specific Histone Recognition by the Bromodomains of Human Coactivators PCAF and CBP/p300
Zeng, L., Zhang, Q., Gerona-Navarro, G., Moshkina, N., Zhou, M.M.(2008) Structure 16: 643-652
- PubMed: 18400184
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2008.01.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2RNW, 2RNX, 2RNY - PubMed Abstract:
Histone lysine acetylation is central to epigenetic control of gene transcription. Bromodomains of chromosomal proteins function as acetyl-lysine (Kac) binding domains. However, how bromodomains recognize site-specific histones remains unanswered. Here, we report three three-dimensional solution structures of the bromodomains of the human transcriptional coactivators CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF) bound to peptides derived from histone acetylation sites at lysines 36 and 9 in H3, and lysine 20 in H4. From structural and biochemical binding analyses, we determine consensus histone recognition by the bromodomains of PCAF and CBP, which represent two different subgroups of the bromodomain family. Through bromodomain residues in the ZA and BC loops, PCAF prefers acetylation sites with a hydrophobic residue at (Kac+2) position and a positively charged or aromatic residue at (Kac+3), whereas CBP favors bulky hydrophobic residues at (Kac+1) and (Kac+2), a positively charged residue at (Kac-1), and an aromatic residue at (Kac-2).
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Structural and Chemical Biology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York University, New York, NY 10029, USA.