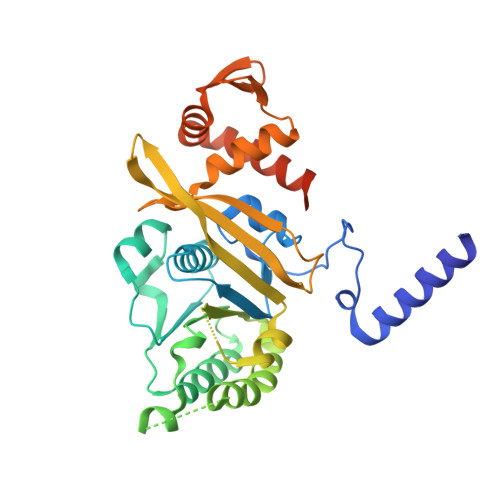
The structure of the E. coli recA protein monomer and polymer.
Story, R.M., Weber, I.T., Steitz, T.A.(1992) Nature 355: 318-325
- PubMed: 1731246
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/355318a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2REB - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the recA protein from Escherichia coli at 2.3-A resolution reveals a major domain that binds ADP and probably single- and double-stranded DNA. Two smaller subdomains at the N and C termini protrude from the protein and respectively stabilize a 6(1) helical polymer of protein subunits and interpolymer bundles. This polymer structure closely resembles that of recA/DNA filaments determined by electron microscopy. Mutations in recA protein that enhance coprotease, DNA-binding and/or strand-exchange activity can be explained if the interpolymer interactions in the crystal reflect a regulatory mechanism in vivo.
- Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06511.
Organizational Affiliation: