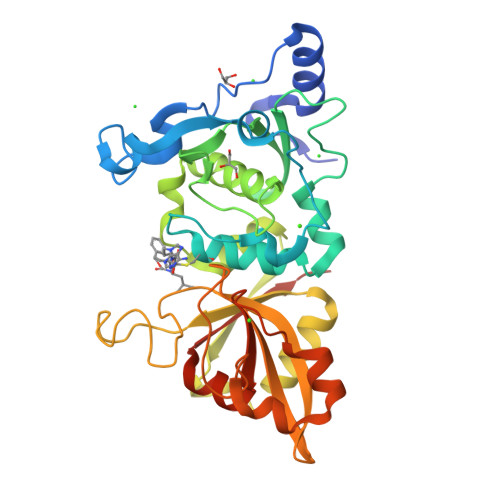
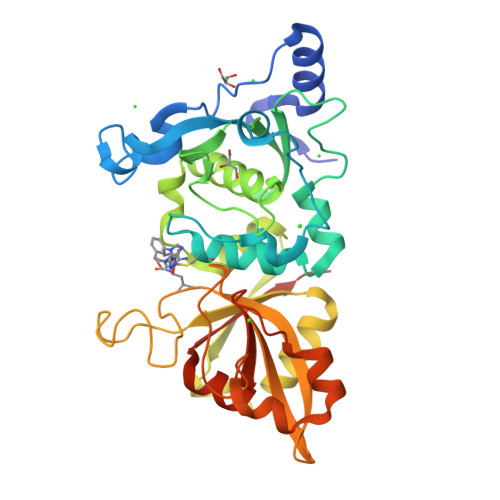
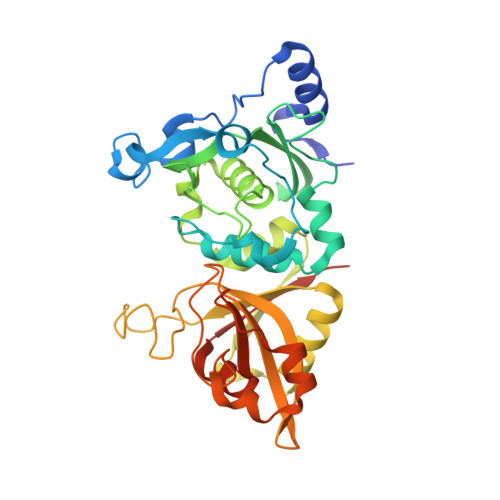
Cocrystal structures of primed side-extending alpha-ketoamide inhibitors reveal novel calpain-inhibitor aromatic interactions.
Qian, J., Cuerrier, D., Davies, P.L., Li, Z., Powers, J.C., Campbell, R.L.(2008) J Med Chem 51: 5264-5270
- PubMed: 18702462
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm800045t
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2R9C, 2R9F - PubMed Abstract:
Calpains are intracellular cysteine proteases that catalyze the cleavage of target proteins in response to Ca(2+) signaling. When Ca(2+) homeostasis is disrupted, calpain overactivation causes unregulated proteolysis, which can contribute to diseases such as postischemic injury and cataract formation. Potent calpain inhibitors exist, but of these many cross-react with other cysteine proteases and will need modification to specifically target calpain. Here, we present crystal structures of rat calpain 1 protease core (muI-II) bound to two alpha-ketoamide-based calpain inhibitors containing adenyl and piperazyl primed-side extensions. An unexpected aromatic-stacking interaction is observed between the primed-side adenine moiety and the Trp298 side chain. This interaction increased the potency of the inhibitor toward muI-II and heterodimeric m-calpain. Moreover, stacking orients the adenine such that it can be used as a scaffold for designing novel primed-side address regions, which could be incorporated into future inhibitors to enhance their calpain specificity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, K7L 3N6, Canada.