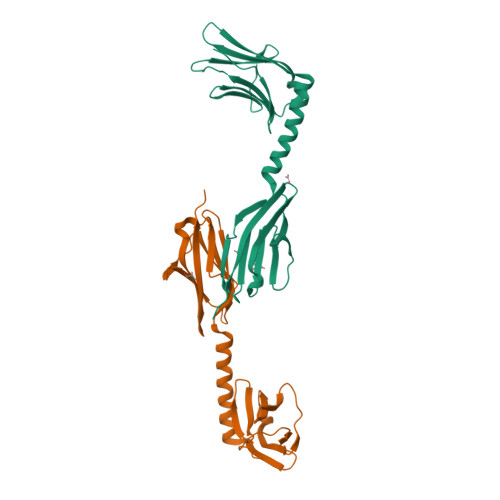
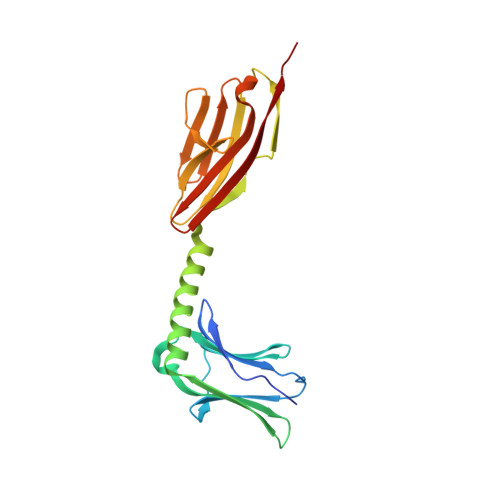
Molecular basis of the C-terminal tail-to-tail assembly of the sarcomeric filament protein myomesin.
Pinotsis, N., Lange, S., Perriard, J.C., Svergun, D.I., Wilmanns, M.(2008) EMBO J 27: 253-264
- PubMed: 18059477
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601944
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2R15 - PubMed Abstract:
Sarcomeric filament proteins display extraordinary properties in terms of protein length and mechanical elasticity, requiring specific anchoring and assembly mechanisms. To establish the molecular basis of terminal filament assembly, we have selected the sarcomeric M-band protein myomesin as a prototypic filament model. The crystal structure of the myomesin C-terminus, comprising a tandem array of two immunoglobulin (Ig) domains My12 and My13, reveals a dimeric end-to-end filament of 14.3 nm length. Although the two domains share the same fold, an unexpected rearrangement of one beta-strand reveals how they are evolved into unrelated functions, terminal filament assembly (My13) and filament propagation (My12). The two domains are connected by a six-turn alpha-helix, of which two turns are void of any interactions with other protein parts. Thus, the overall structure of the assembled myomesin C-terminus resembles a three-body beads-on-the-string model with potentially elastic properties. We predict that the found My12-helix-My13 domain topology may provide a structural template for the filament architecture of the entire C-terminal Ig domain array My9-My13 of myomesin.
Organizational Affiliation:
EMBL-Hamburg c/o DESY, Hamburg, Germany.