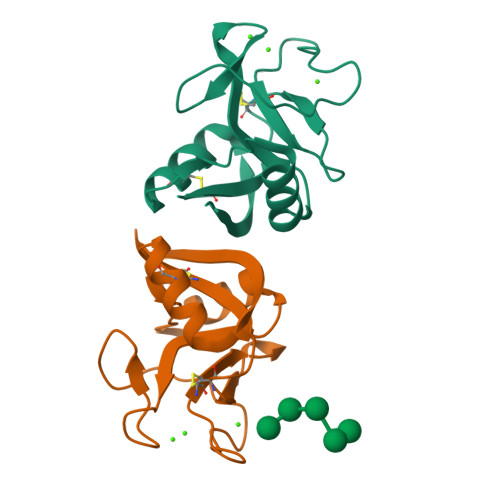
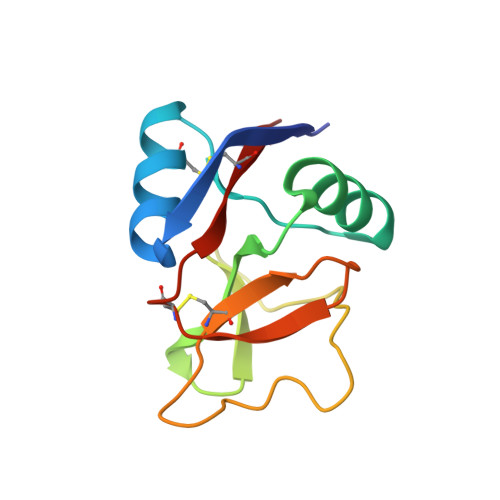
Structure of a C-type mannose-binding protein complexed with an oligosaccharide.
Weis, W.I., Drickamer, K., Hendrickson, W.A.(1992) Nature 360: 127-134
- PubMed: 1436090
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/360127a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MSB - PubMed Abstract:
C-type (Ca(2+)-dependent) animal lectins such as mannose-binding proteins mediate many cell-surface carbohydrate-recognition events. The crystal structure at 1.7 A resolution of the carbohydrate-recognition domain of rat mannose-binding protein complexed with an oligomannose asparaginyl-oligosaccharide reveals that Ca2+ forms coordination bonds with the carbohydrate ligand. Carbohydrate specificity is determined by a network of coordination and hydrogen bonds that stabilizes the ternary complex of protein, Ca2+ and sugar. Two branches of the oligosaccharide crosslink neighbouring carbohydrate-recognition domains in the crystal, enabling multivalent binding to a single oligosaccharide chain to be visualized directly.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, Columbia University, New York, New York 10032.