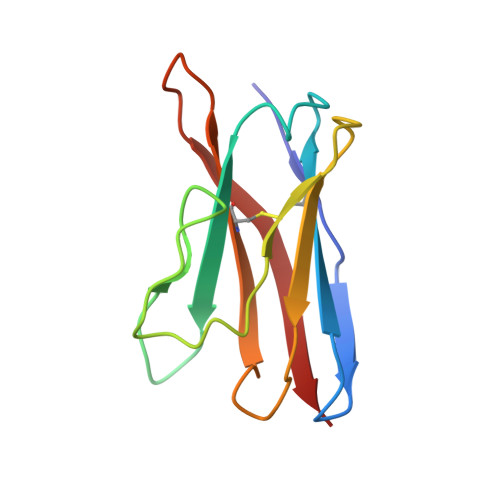
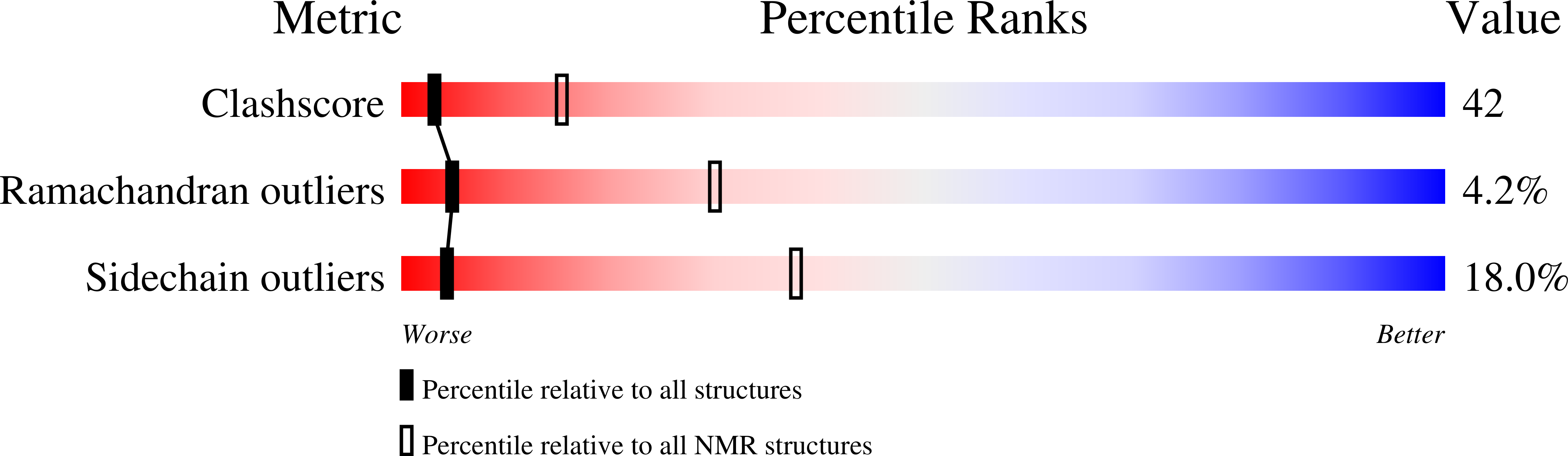Solution structure of 6aJL2 and 6aJL2-R24G amyloidogenics light chain proteins.
Maya-Martinez, R., Gil-Rodriguez, P., Amero, C.(2015) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 456: 695-699
- PubMed: 25522882
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.044
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2MKW, 2MMX - PubMed Abstract:
AL amyloidosis is the most common amyloid systemic disease and it is characterized by the deposition of immunoglobulin light chain amyloid fibers in different organs, causing organ failure. The immunoglobulin light chain germinal line 6a has been observed to over-express in AL patients, moreover, it was observed that, out of these amyloidogenic proteins, 25% present a mutation of an Arg to Gly in position 24. In vitro studies have shown that this mutation produces proteins with a higher amyloid fiber propensity. It was proposed that this difference was due, in part, to the formation of a non-canonical structural element. In order to get a more detailed understanding of the structural and dynamic properties that govern the amyloid fibers formation process, we have determined the solution structure by NMR for the two constructs, showing that the difference in amyloid fibril formation is not due to sequence or structure.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratorio de Bioquímica y Resonancia Magnética Nuclear, Centro de Investigaciones Químicas, Universidad Autónoma del Estado de Morelos, Cuernavaca, Mexico.