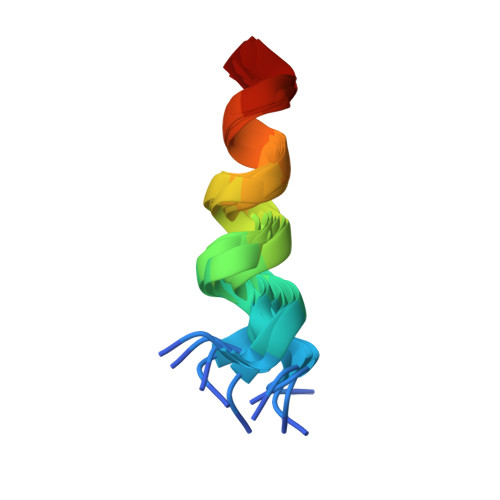
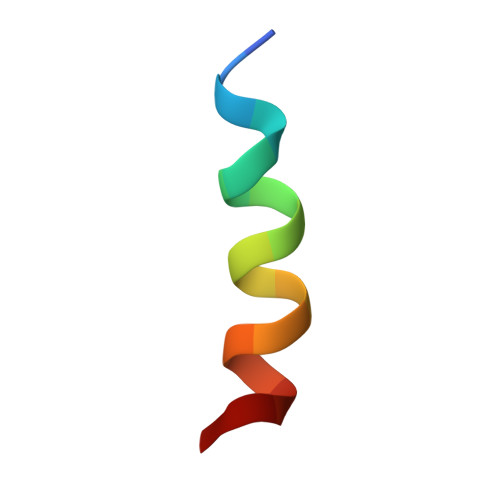The N Termini of a-Subunit Isoforms Are Involved in Signaling between Vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) and Cytohesin-2.
Hosokawa, H., Dip, P.V., Merkulova, M., Bakulina, A., Zhuang, Z., Khatri, A., Jian, X., Keating, S.M., Bueler, S.A., Rubinstein, J.L., Randazzo, P.A., Ausiello, D.A., Gruber, G., Marshansky, V.(2013) J Biological Chem 288: 5896-5913
- PubMed: 23288846
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.409169
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2LX4 - PubMed Abstract:
Previously, we reported an acidification-dependent interaction of the endosomal vacuolar H(+)-ATPase (V-ATPase) with cytohesin-2, a GDP/GTP exchange factor (GEF), suggesting that it functions as a pH-sensing receptor. Here, we have studied the molecular mechanism of signaling between the V-ATPase, cytohesin-2, and Arf GTP-binding proteins. We found that part of the N-terminal cytosolic tail of the V-ATPase a2-subunit (a2N), corresponding to its first 17 amino acids (a2N(1-17)), potently modulates the enzymatic GDP/GTP exchange activity of cytohesin-2. Moreover, this peptide strongly inhibits GEF activity via direct interaction with the Sec7 domain of cytohesin-2. The structure of a2N(1-17) and its amino acids Phe(5), Met(10), and Gln(14) involved in interaction with Sec7 domain were determined by NMR spectroscopy analysis. In silico docking experiments revealed that part of the V-ATPase formed by its a2N(1-17) epitope competes with the switch 2 region of Arf1 and Arf6 for binding to the Sec7 domain of cytohesin-2. The amino acid sequence alignment and GEF activity studies also uncovered the conserved character of signaling between all four (a1-a4) a-subunit isoforms of mammalian V-ATPase and cytohesin-2. Moreover, the conserved character of this phenomenon was also confirmed in experiments showing binding of mammalian cytohesin-2 to the intact yeast V-ATPase holo-complex. Thus, here we have uncovered an evolutionarily conserved function of the V-ATPase as a novel cytohesin-signaling receptor.
Organizational Affiliation:
Center for Systems Biology, Program in Membrane Biology and Division of Nephrology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts 02114, USA.