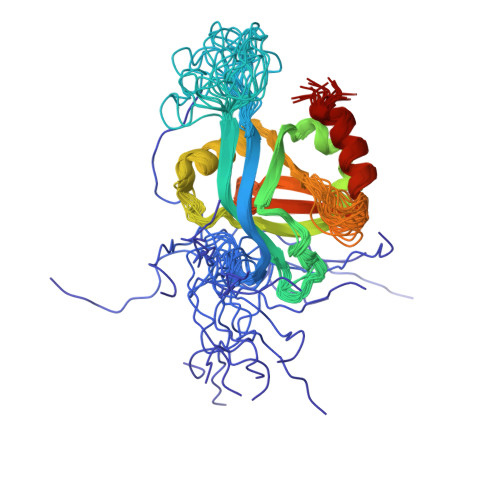
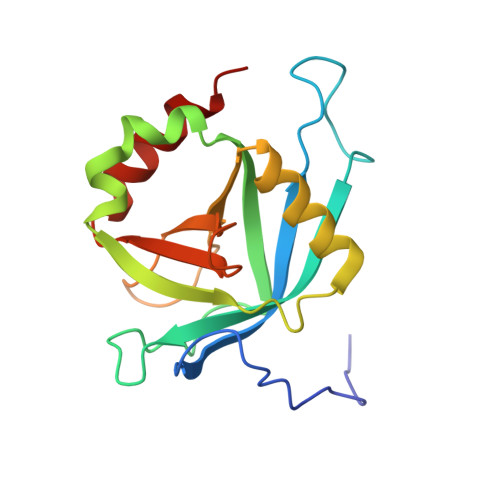
Solution NMR structure of MED25(391-543) comprising the activator-interacting domain (ACID) of human mediator subunit 25.
Eletsky, A., Ruyechan, W.T., Xiao, R., Acton, T.B., Montelione, G.T., Szyperski, T.(2011) J Struct Funct Genomics 12: 159-166
- PubMed: 21785987
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10969-011-9115-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2L6U - PubMed Abstract:
The solution NMR structure of protein MED25(391-543), comprising the activator interacting domain (ACID) of subunit 25 of the human mediator, is presented along with the measurement of polypeptide backbone heteronuclear 15N-{1H} NOEs to identify fast internal motional modes. This domain interacts with the acidic transactivation domains of Herpes simplex type 1 (HSV-1) protein VP16 and the Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) major transactivator protein IE62, which initiate transcription of viral genes. The structure is similar to the β-barrel domains of the human protein Ku and the SPOC domain of human protein SHARP, and provides a starting point to understand the structural biology of initiation of HSV-1 and VZV gene activation. Homology models built for the two ACID domains of the prostate tumor overexpressed (PTOV1) protein using the structure of MED25(391-543) as a template suggest that differential biological activities of the ACID domains in MED25 and PTOV1 arise from modulation of quite similar protein-protein interactions by variable residues grouped around highly conserved charged surface areas.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, The State University of New York at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY 14260, USA.